There are several misperceptions about American manufacturing that I will clarify in this article.
The first misperception is Manufacturing is in inevitable decline.
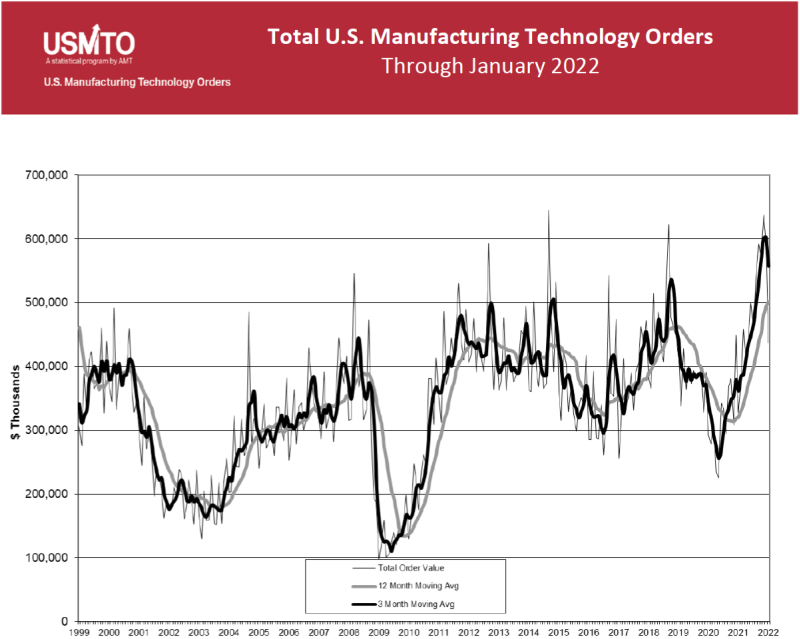
Evidence that this is not true is provided by the latest U.S. Manufacturing Technology Orders Report published by the Association For Manufacturing Technology AMT on March 14, 2022. It states, “Manufacturing technology orders totaled $436.6 million in January 2022…January orders were also the strongest on record since USMTO began tracking orders.
The United States still maintains its second position as the world’s largest manufacturing country by a substantial lead over Japan at third place.
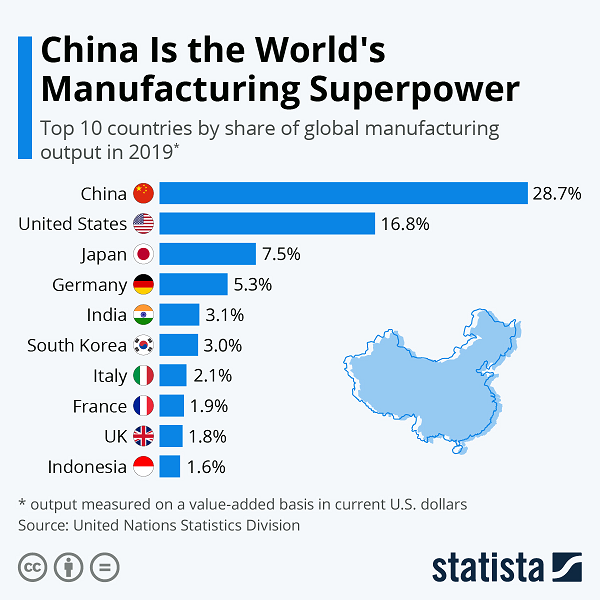
U.S. can’t compete with China
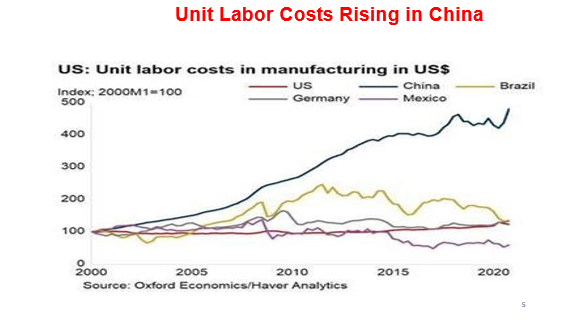
First, rising wages in China are helping U.S. manufacturers be more competitive in the global marketplace.
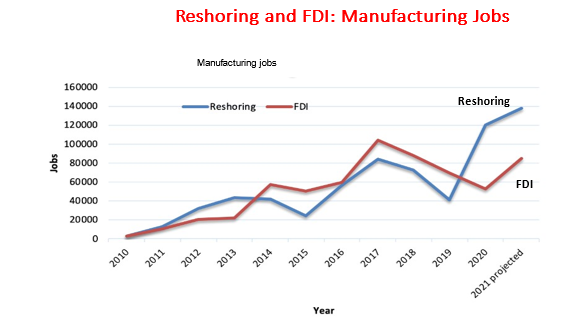
Second,the Total Cost of Ownership Worksheet calculator developed by Harry Moser’s Reshoring Initiative is helping more and more American manufacturers be competitive domestically so they can reshore manufacturing from overseas back to America. The TCO worksheet is available for free at www.reshorenow.org., According to data provided by the Reshoring Initiative, we regained one million jobs through reshoring and foreign direct investment between 2010 to 2021.
Manufacturing doesn’t pay wages for a middle-class family life
According to the National Association for Manufacturers, “average hourly earnings of production and nonsupervisory workers in manufacturing rose 0.5% from $24.37 in December to $24.48 in January, up from $23.27 in January 2021.” While these wages for production workers may be as low as some retail and service jobs, the wages for skilled workers range from $60,000 to $80,000/year. Salary and supervisory workers in manufacturing “earned $92,832 on average, including pay and benefits.”
The reality is that skilled trade jobs provide an excellent career opportunity for those looking for a stable, high-demand, high-paying job. Workers with the skills needed by manufacturers are in high demand. There were 856,000 manufacturing job openings in December. It was the ninth straight month with openings that have exceeded 800,000, with job postings remaining well above pre-pandemic levels.” The manufacturing industry has forecasted to have 2.1 million unfilled jobs by 2030.
According the 4th quarter 2021 Manufacturer Outlook Survey, “85.2% had unfilled positions within their companies for which they were struggling to find qualified applicants. Companies were addressing the skills shortage by creating or expanding internal training programs (62.7%), utilizing temporary staffing services (50.4%), collaborating with educational institutions on skills certification programs (41.2%) and encouraging possible retirees to stay longer in their roles (39.9%) …”
Manufacturing jobs are boring, dirty, and dangerous
While one picture is worth a thousand words, I can’t include enough pictures in this article to disprove this misperception. I will, however, explain why manufacturing jobs are not as boring, dirty, and dangerous as they previously were.
First, Congress created the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) as part of the Department of Labor to ensure safe and healthful working conditions for workers by setting and enforcing standards and by providing training, outreach, education and assistance. “Under the provisions of the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 (OSH Act), employers must provide a workplace free from recognized hazards that are causing, or are likely to cause, death or serious physical harm to employees regardless of the size of business.” OSHA standards cover hazardous chemicals and materials, machine operation, machine guarding, electrical hazards, fall protection, sanitation, indoor air quality, drinking water, ergonomic guidelines, temperature & weather, personal protective equipment, etc.
Second, in the past 20 years, there have been standards established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that cover quality Management, Information Security, Occupational Health and Safety, Medical Devices, among many others. It has become common for companies to be required to get certified that they meet these standards in order to become a vendor or service provider. Aircraft companies and their supply chain are required to be certified to AS9100, and automobile manufacturers are required to meet TS 16949 standards.
Third, the use of automation, robots, cobots, and sensors are reducing dangerous and physically difficult tasks in manufacturing. The difference between robots and cobots is that robots are programmed to perform a standalone function and cobots are design to partner with a person to perform a function.
For example, a robot can pick up a slab of hot glass off the production line in making sheet glass and place the sheet in a stack. Robots have taken over dipping and swirling a sprue loaded with wax parts into the ceramic slurry to make an investment casting. A cobot can rotate a part to allow a person to perform a task, such as assembly of a transmission on an automobile production line. Sensors can detect whether a person’s hand or other body part is in the way of a machine operation and stop the machine. All stamping machines have such sensors to make sure a person’s hand is out of the way before the punch press stamps out the metal part.
Fourth, processes that would be very boring for a person to do repetitively have been automated. Some examples are cutting wire to be inserted into a plastic molding part, filling or sealing a plastic bag or bottle, placing labels on bottles, containers, and boxes, as well as placing components on a printed circuit board.
Although many businesses have labeled these standards as too onerous and expensive, there is no doubt that they have dramatically enhanced the health and safety of American manufacturing workers.
Shifting the Narrative from ‘Inevitable Decline” to ‘Vibrant Opportunity.”
Now that we’ve clarified the common misperceptions about manufacturing, let me introduce you to a vision for the future. I am now a founding member with Doug Berger of a new non-profit organization, Industry Reimagined 2030. The vision of Industry Reimagined 2030 is to bring about a generational sea-change in U.S. Industry from a prevailing worldview of “inevitable decline” to one of “‘vibrant opportunity.”
Thinking at a national scale is different than thinking at a national level. Policy is at the national level. Scaling successful initiatives at a local level to thousands of communities is thinking at a national scale. In this regard, there are many local successes that I have written about previously that aren’t being scaled.
We are thinking from the future-back for these bold outcomes … standing in the gap to today and asking “What is missing?” “What needs to happen?” In this regard, we are advancing the idea of Reimagine Dialogues to engage people to be imaginative first and then develop practical action steps to close the gap.
By 2030 U.S. manufacturing will be revitalized, globally competitive and advancing societal interests. There will be:
- 50,000 world-class domestic manufacturers (10x increase)
- Additional 5 million to the manufacturing-related, middle-income workforce (40%)
- Environmental footprint to supply U.S. goods reduced by 30%
- Consumer purchases of US made goods increased by $500 million
It will take unprecedented collaboration between ourselves and other organizations to achieve this vision. If you support the concept of these Reimagine Dialogues, please contact me at michele@savingusmanufacturing.com.
Tags: American manufacturing