Over 150 countries in the world have shifted a significant portion of their tax mix to border adjustable consumption taxes – value added taxes (VATs) or goods and services taxes (GSTs). Consumption taxes are “border adjustable taxes” and allowed under World Trade Organization rules. Consumption taxes are a tax on consumption – as opposed to income, wealth, property, or wages. Consumption taxes are called goods and services taxes in Canada, Australia, New Zealand or value added taxes in other countries. They are usually a tax only on the incremental value that is added at each level of the supply chain to a product, material or service. Most countries VATs or GSTs are tariff and subsidy replacements, mimicking a currency devaluation if a country raises the VAT or GST and uses proceeds to lower purely domestic taxes and costs.
After 40 years of multilateral tariff reduction, other countries replaced tariffs with VATs but the U.S. did not. American exporters face nearly the same border taxes (tariffs + consumption tax) as they did in the early 1970s. Foreign VATs are export subsidies as they are rebated to companies that export their goods. For example:
- Mexico established a 15% VAT after NAFTA
- Central American countries established a 12% VAT after CAFTA
- Germany raised its VAT to 19% in 2007 to fund business tax reduction for trade competitiveness
The rates range from 12% to 24% and average 17% globally. This means that virtually all foreign countries tax our exports at 17% on top of tariffs. They subsidize domestic shipments abroad with the average 17% tax rebate. The figure below illustrates how it works.
| U.S. Local Price = $100
|
China Local Price = $100
|
| U.S. Price PLUS 17% VAT = $117.00
|
Chinese Price MINUS 17% VAT rebate = $85.47
|
The map below shows which nations have consumption taxes (red) and which do not (blue).
Because foreign consumption taxes are border adjustable, companies that export are double taxed. They pay U. S. taxes and the foreign border tax. Importers can sell cheaper products because they receive a consumption tax rebate from their home country and do not pay U. S. VAT.
Eliminate Payroll Tax Burden with the most efficient VAT in world
In written testimony to the House Ways and Means Committee of the U. S. House of Representatives on May 18, 2017, the Coalition for a Prosperous America (CPA) recommended “a new border adjustable consumption tax (Goods and Services Tax) that funds a full credit against all payroll taxes.”
Highlights from the testimony paraphrased or quoted include: “A new U.S. goods and services tax (GST) of approximately 12% should be enacted to shift taxation to consumption using the credit/invoice method. The proceeds should be credited against payroll taxes paid by all workers and businesses. GST proceeds should be applied as a full credit against the 15.3% rate of payroll taxes to reduce the cost of labor in the US while increasing after tax wages.
Exported goods and services would receive a full rebate. Imports would pay the GST. Small business with less than, for example, one million dollars could be exempted without sacrificing significant tax revenue.”
CPA’s written testimony explained, “Domestic prices vs. wages would not worsen because the payroll tax is embedded in the cost of all goods and services. Thus, eliminating the payroll tax lowers the prices for goods and services or increases wages depending upon the particular competitive forces in each product sector. A GST raises goods and services prices, but the GST/payroll tax combination would largely cancel each other out thereby holding the domestic economy harmless.
The more modern GSTs implemented by free market economies are in Canada, Australia and New Zealand. The compliance and administration burdens are relatively low in comparison to other taxation methods. The U. S. can learn from those and other countries’ experiences to implement the most modern, streamlined GST in the world.”
In summary, the proposed GST would
- Reduce the cost of labor in the U. S.
- Give every worker a raise
- Lower price of U/ S. exports
- Levy a tax on imports
The following are some of the benefits of a payroll tax credit for manufacturers, ranchers, and farmers:
- Regressiveness of VAT offset by elimination of regressive payroll tax
- VAT costs on all domestic producers are offset
- No impact on prices of domestic goods/services
- Imported goods/services prices increase
- Cost of production for exports reduced
Change to a Sales Factor Apportionment (SFA) Border Adjustable Profit Tax
Last year, I wrote an article about corporate tax reform at the federal level based on the Sales Factor Apportionment Framework proposed by one of the members of the Coalition for a Prosperous America, Bill Parks. Mr. Parks is a retired finance professor and founder of NRS Inc., an Idaho-based paddle sports accessory maker. He asserted that “Tax reform proposals won’t fix our broken corporate system… [because] they fail to fix the unfairness of domestic companies paying more tax than multinational enterprises in identical circumstances.”
He explained that multinational enterprises (MNEs) can use cost accounting practices to transfer costs and profits within the company to achieve different goals. “Currently MNEs manipulate loopholes in our tax system to avoid paying U. S. taxes… MNEs can legitimately choose a cost that reduces or increases the profits of its subsidiaries in different countries. Because the United States is a relatively high-tax country, MNEs will choose the costs that minimize profits in the United States and maximize them in what are usually lower-tax countries.”
The way his plan would work is that the amount of corporate taxes that a multinational company would pay “would be determined solely on the percent of that company’s world-wide sales made to U. S. customers. Foreign MNEs would also be taxed the same way on their U. S. income leveling the playing field between domestic firms and foreign and domestic MNEs.”.
The Board of the Directors of the Coalition for a Prosperous America chose to support Sales Factor Tax Apportionment and included the following in their testimony to the House Ways and Means Committee:
“The US corporate tax system harms America’s trade competitiveness, overtaxes income from wages, under taxes consumption, and is bad at actually collecting what is owed. It also enables rampant base erosion through transferring profits to tax havens or countries with lower corporate tax rates. Full reform centered around destination based, border adjustment principles can result in an efficient, trade competitive, and largely tamper-proof tax system.
SFA is a destination based profit tax. Pretax income is allocated to the US in proportion to the percentage of a company’s total sales in the U. S. Pre-tax income earned outside the US is not taxed. Tax rates can be lowered substantially while still meeting revenue targets.”
The Coalition for a Prosperous America favors “a border adjustable business tax (for all entity types) which allocates pre-tax income based upon the destination of sales. Formulary apportionment based upon a single sales factor (sales factor apportionment or SFA) is well established at the state level. It solves most of the base erosion/profit shifting and tax haven abuse problems facing tax writing committees. SFA eliminates the disparate tax treatment between domestic companies (who pay the full income tax burden on worldwide income), multinationals (many of which shift profits to tax havens), and foreign companies (which pay a territorial income tax).
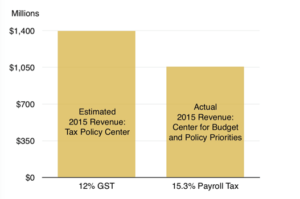
A broad based 12% GST could raise $1.4 trillion in new revenue. Payroll tax revenue in 2015 was 33% of total tax revenue at $1.056 trillion.”
CPA asserts that U. S. “trade competitiveness would be substantially improved because exports are freed from both the GST and payroll tax burden. Imports never include the cost of the U. S. payroll tax, but would pay the GST. This effect has been called Fiscal Devaluation because it mimics a currency devaluation for trade purposes. It only works if you combine a new GST with a ubiquitous domestic tax or cost reduction. The optimal domestic tax reduction is the payroll tax burden.”
The reason for CPA’s support is that “SFA taxes pre-tax income allocated to the U. S. but not profits allocated to foreign sales. Domestic firms can legitimately ‘avoid’ taxation by exporting more. Profits from imports are subject to tax. Domestic, multinational and foreign firms are on an equal tax footing.
The current corporate tax system cannot be fixed because it allows the fiction of intra-firm transactions to erode the tax base. Multinational companies use them to self-deal, strictly for tax purposes, shifting income to tax haven jurisdictions. Companies sell products or services to themselves, governed only by an ‘arm’s length’ principle which allows them to create their own pricing terms subject to a nearly unenforceable ‘fair market value’ constraint.
The intra-company transactions are not free market, ‘arm’s length’ or true third-party transactions. The only economically meaningful ‘sale’ is one to a true third party outside the company. As much of 30% of tax revenue may be lost from profit shifting to tax haven jurisdictions which have effective tax rates of 0-4%. These include Bermuda, Netherlands, UK Caribbean Islands, Ireland, Luxembourg, Singapore, and Switzerland.”
The CPA testimony provides the following example: “Assume a multinational corporation has worldwide sales of $100 billion, $50 billion sales in the U. S. and company-wide pretax income of $10 billion. Fifty percent of the profits, under SFA, are apportioned to the US. So, the profits to be taxed in the USA in this case are $5 Billion. Using a 20% corporate tax rate yields a SFA tax of $1 billion. Intra-company transactions with a Bermuda subsidiary would be irrelevant.
Merely lowering the U. S. corporate tax rate for example to 15% without further reform would not eliminate the tax competition with tax haven jurisdictions. SFA would make tax havens irrelevant because true sales to any foreign country would be ignored. IRS litigation centered around the proper fair market value of intra-firm transactions would disappear. Only profits allocated to the US in proportion to true third-party sales would be taxable.”
CPA asserts that “SFA would allow a significant reduction in the business tax rate while collecting similar revenue because base erosion is largely fixed. By one estimate, a 13% corporate tax rate under SFA would collect the same revenue as the current system…”
In conclusion, CPA recommends, “The U. S. tax system should shift to more border adjustability through destination based taxation. If the House GOP Blueprint does not gain Senate or White House support, the Ways and Means Committee has solid alternatives to meet their goals. CPA supports enacting (1) a new GST to fund a full credit against payroll taxes, plus (2) a shift to sales factor apportionment of global profits as an alternative to our current corporate income tax system.”
We need to take bold action if we want to rebuild our manufacturing industry to create jobs and prosperity. As I visit district offices of our California Congressional delegation as chair of the California chapter of CPA, I am encouraged by the interest these recommendations for tax reform are generating on a bi-partisan basis.