The recent opinion article by Kenneth A. Reinert titled “Time to end America’s obsession with manufacturing” posted on Microsoft Start presents several reasons why our “obsession with manufacturing is misplaced” in his opinion This article will focus on why manufacturing is important to the U.S. economy and why we need to be obsessed by manufacturing.
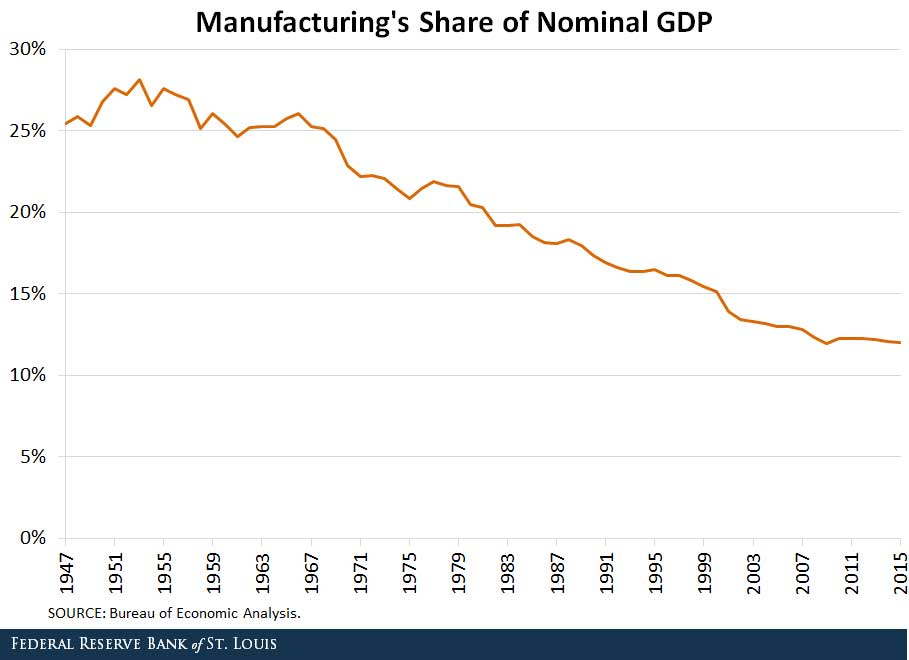
His first reason is that “for the high-income countries of the world, the share of manufacturing as a percent of gross domestic product (GDP) is currently approximately 13 percent. In the U.S., it is approximately 11 percent, very close to the average of high-income countries.” In comparison, Germany’s manufacturing industry was
22.2 %, China was 28.4 %, and Japan was 20.6 % with the world average being 17.5 % in 2021, which was more like the percentage the U.S. previously had prior to so much manufacturing being offshored to Asia.
His second reason is that “in high-income countries, the share of the labor force in manufacturing …the share is approximately 13 percent. In the United States, it is approximately 8 percent. This reflects the increased labor productivity in American manufacturing.”
Even at this low percentage, manufacturing still “drives 20 percent of capital investment, 30 percent of productivity growth, 60 percent of exports, and 70 percent of business R&D.”
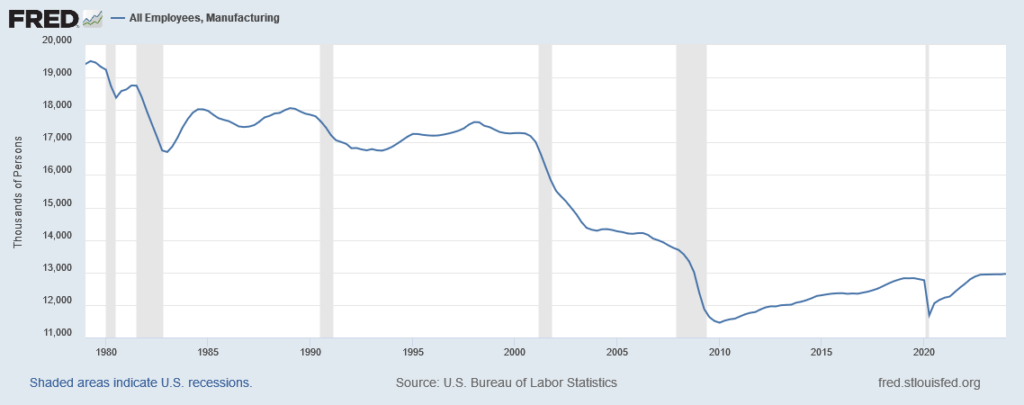
Manufacturing employment was relatively constant from 1960 through 1990, but began declining in the late 1990s. However, manufacturing employment was at an all-time peak of 19.6 million in June 1979, representing 22 percent of the labor force. The biggest drop in employment occurred from 2000 – 2010 after China was granted Most Favored Nation status, and American manufacturers started offshoring manufacturing overseas to China. One-third of U.S. manufacturing workers (5.8 million people) lost their jobs as shown by the chart below:
Thirdly, Reinert says that ”services, or more precisely producer services, are at the heart of the increase in manufacturing productivity. Economists and business analysts have noted the increased “servitization” of manufacturing; it is now very difficult to disentangle manufacturing from producer services given their symbiotic relationship.” The problem with this reasoning is that the less manufacturing that is done in the U.S., the fewer producer services you have to offer domestically and for export. Services are even easier to offshore than manufacturing, so it is no surprise that many technical services in IT, customer service and communication have been offshored to India in particular.
His fourth reason is “manufacturing can no longer be envisioned as a single stage. Rather, it is spread out over multiple stages and countries in complicated global value chains (GVCs), held together by, you guessed it, producer services: transport, logistics, information and communication technologies, insurance and many others. Rather than a single stage, manufacturing is now a network.”
The global value chains are exactly what caused the supply chain disruptions and shortages during the COVID pandemic. Manufacturers learned that they can’t be dependent on components and parts being shipped from overseas to the U.S. to be assembled into their products. This is one of the main reasons more manufacturers are reshoring manufacturing to the U.S. Moreover, as a country, we can’t be dependent on another country, particularly China, for the components and parts that go into products for our defense and national security industries as well as our pharmaceutical and medical supply industries.
His fifth reason is that “what really matters for economic success is high value added… high value added tends to be found at the beginning and end of GVCs, in research and development, branding, design, distribution, marketing and after-sales services. The actual assembly stage of GVCs is often where the least value added is to be found.” The error of this reasoning is that R & D, distribution, and after-sales services have also been offshored to other countries so that our exports of advanced technology products has also been reduced. In fact, “the trade deficit in advanced technology products is accelerating, growing from $128 billion in 2019, to $195 billion in 2021, to $244 billion in 2022.”
Reinert opines that “U.S. is currently involved in a bipartisan experiment to throw “an extraordinary amount of subsidies at particular manufacturing sectors, including semiconductors and green energy. Estimates of the total subsidies reach as high as $1 trillion. Manufacturing subsidies area way of being seen to be “doing something” in the economic realm and signal “standing up to China.”
His conclusion is that “We need to end our obsession with manufacturing and focus on high value added wherever it is found. We also need to limit manufacturing subsides and allow them to be subject to WTO disciplines that the U.S. has developed and utilized intensively. Otherwise, long-run growth and prosperity will be diminished.”
The only correct opinion in his article is that “national security requires producer services along with manufacturing. There is a saying among military analysts that “amateurs talk strategy, but experts talk logistics.” These “logistics” are producer services. In the words of one researcher, these include “the construction, maintenance and operation of military bases; equipment maintenance; food service; transportation; communications and IT support; and supply chain management.” This is exactly why we need to strengthen our domestic manufacturing supply chain of goods and materials needed by our military and our defense industry and not a reason to end our obsession with manufacturing.
Last week, I discussed this article with a friend who is a fellow member of the Coalition for a Prosperous America, Dr. John R. Hansen. He is a retired economist who worked with the World Bank for over 30 years. We agreed with Reinert that using subsidies to drive manufacturing growth with can be expensive and wasteful, but believe he is wrong to dismiss the importance of manufacturing to America and wrong to assume that massive subsidies would be required for a renaissance in American manufacturing. I asked him to email me a few comments on Reinert’s article that I could include in my article. He wrote:
“The importance of manufacturing for America lies in the following: We need to be able to produce and export internationally tradeable goods to pay for the goods we import. For the past two years, our trade deficit in goods has exceeded 1.0 trillion USD. Yes, we could continue borrowing and printing money to cover our trade deficits, but this is a dead-end strategy. The only sustainable strategy is to develop our ability to produce a surplus of internationally tradeable goods.
Producing more services is not the answer. They tend to be very labor intensive, and we cannot compete against countries like India where well-educated people receive very low wages compared to the average American. Furthermore, most services require physical presence.
The services highlighted by Reinhart suffer the same problems. They are very hard to export, especially if you don’t produce enough tradeable exports like manufactured goods into which the services can be embedded.
Our only real hope of paying for the imports we need is to first increase the production of tradeable manufactured and agricultural goods before we can stimulate the production of services that can be embedded in these goods. Both are highly tradeable, and we have a basic comparative advantage in both. We have abundant agricultural land, much of which is supplied with high technology that helps offset our higher labor costs. We also have one of the most advanced manufacturing sectors in the world.
The main reason we cannot reduce our imports and increase our exports of manufactured goods is that other countries producing such goods have currencies that are seriously undervalued compared to the US dollar. For example, the currencies of China and Japan, two of our biggest competitors and sources of trade deficits, have currencies that are undervalued by 40% and 60% against the US dollar. This makes the prices of the goods that these countries produce 40-60% lower than if the foreign currencies were valued at exchange rates that would balance trade.”
John and I agree that the only real solution to this problem is the Market Access Charge that John has proposed and I have written about in several previous articles. The MAC would do this by imposing a small charge that would be collected on all foreign-source money entering America’s financial market (averaging USD 90 trillion every year) For more details, read my article , “Why a Market Access Charge is Urgently Needed,” from this past January.
We need to stop the destruction of American industry and innovation, the loss of high-paying manufacturing jobs, and the collapse of communities. We need to rebuild American manufacturing to create prosperity for our children and grandchildren.