The third reason why manufacturing is important is that the United States is still a top leader in generating manufacturing exports. The U.S. was the world’s largest exporter until 1992, when Germany took over this position. The U.S. maintained a position as the second-highest exporter, until China surpassed it in 2008. Germany remained number one until 2009, when China surpassed it to become the world’s top exporter. The U.S. overtook Germany as the second-highest exporter in 2014. The latest data for world exports is from 2019 when China’s exports totaled $1.8 trillion, down from $2.49 trillion in 2018; the U.S. exports totaled $1.24, down from $1.66 trillion in 2018, and Germany’s exports were $1.12, down from $1.55 trillion in 2018.

According to a 2020 report on exports: ”The following export product groups categorize the highest dollar value in American global shipments during 2019. Also shown is the percentage share each export category represents in terms of overall exports from the United States.
- Machinery including computers: $205.9 billion (12.5% of total exports)
- Mineral fuels including oil: $199.7 billion (12.1%)
- Electrical machinery, equipment: $173.2 billion (10.5%)
- Aircraft, spacecraft: $136 billion (8.3%)
- Vehicles: $133 billion (8.1%)
- Optical, technical, medical apparatus: $90.8 billion (5.5%)
- Plastics, plastic articles: $64.9 billion (3.9%)
- Gems, precious metals: $59.6 billion (3.6%)
- Pharmaceuticals: $53.6 billion (3.3%)
- Organic chemicals: $39.3 billion (2.4%)
America’s top 10 exports surpass well over two-thirds (70.3%) of the overall value of its global shipments.”
Manufactured goods “make up more than 66% of U.S. exports…One-third of exported goods are capital goods double the level of 20 years ago… Only 12% of U.S. exported goods are consumer goods…Just 8% of exported goods are foods, feeds, and beverages ($131 billion). The big three are soybeans ($20 billion), meat and poultry ($20 billion), and corn ($9 billion).”
According to the U.S. Small Business Administration, small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) comprised 97 percent of all identified U.S. exporters, generated 64 percent of net new jobs between 1992 to 2009, and represented 31 percent of U.S. export value in 2008. About 65 percent of all U.S. exports come from small businesses with fewer than 20 employees.
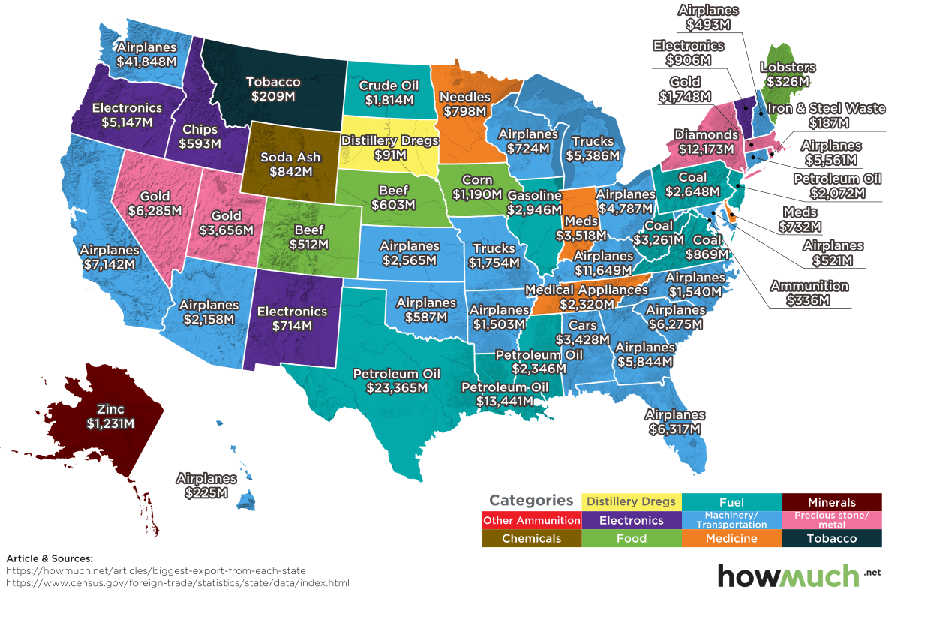
Exports of manufactured goods is important to the economies of most states – even in those areas where manufacturing has declined as a portion of the Gross State Product (GSP).
The top five U. S. export markets:
- Canada
- Mexico
- China
- Japan
- United Kingdom
Both President Bush and President Obama had the goal of doubling U.S. exports during their administrations. President Obama even established the Export Promotion Cabinet by Executive Order 13534 On March 11, 2010 and tasked them with a plan to achieve the goal of doubling U.S. exports in five years that he had presented in his 2010 State of the Union address.
The National Export Initiative (NEI) Executive Order had five components: improve advocacy and trade promotion, increase access to export financing, remove barriers to trade, enforce current trade rules, and promote strong, sustainable, and balanced growth.
The NEI identified eight priorities for the plan, and the Export Promotion Cabinet developed recommendations to address each of these priorities, which covered all five components, cut across many federal government agencies, and focus on areas where concerted federal government efforts can help lift exports.
It was no surprise to me that the plan to double exports in five years was unsuccessful because we are fighting against the predatory mercantilism of countries such as China, India, and Japan. The biggest problem is that the United States is no longer the manufacturing source for consumer and household goods and commodities that it once was. American brands such as IBM, General Electric, and Maytag were known worldwide for their quality and innovation. These types of products are now being made in Asia, mostly in China, and imported by the United States and other countries for their consumers to buy rather than being manufactured in the United States for export worldwide.
The majority of manufacturers that were able to survive the great stampede to offshore manufacturing to China don’t produce a finished product; they are the Tier 2, 3 and 4 suppliers that produce components, parts, and assemblies for Original Equipment Manufacturers. Thus, they don’t have a product to sell for export. I have been representing this type of company as a manufacturers’ sales rep for over 30 years. Most of these companies do not have engineering staff to design a complete product and don’t have the capability to market a product internationally.
I’ve been working with inventors and entrepreneurs of start-up companies for years to help them select the processes and sources for their new products. As a director on the board of the San Diego Inventors Forum, I give a presentation of how to select the right processes and sources for a new product as part of our annual curriculum at our monthly meetings in our program of helping inventors go from product design to market.
If we want to increase our manufacturing exports, we need to help inventors and entrepreneurs develop their products and get them to market. Additive manufacturing has enabled inventors and entrepreneurs to produce low cost prototypes rapidly here in the U.S. The biggest hurdle is to fund the tooling needed to manufacture their products at production volume levels. For advanced technologies that require research and development, there are government funded Small Business Research Grants that enable small start-up companies boot strap their product development. Perhaps, we can create a grant program for inventors and entrepreneurs to fund the tooling and initial production runs of new products.
Remember, Albert Einstein is widely credited with saying, “The definition of insanity is doing the same thing over and over again, but expecting different results.” We aren’t going to increase exports by doing the same things we have been doing for the past 20 years.