The United States gradually lost manufacturing jobs from the peak of 19.5 million in 1979 to 17.3 million by early 2000. However, after China was granted Most Favored Nation status that year, the loss of manufacturing jobs in the U.S. accelerated dramatically as American manufacturers moved manufacturing offshore and cheaper Chinese goods drove U.S. manufacturers out of business. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, we lost 5.8 million manufacturing jobs from the middle of the year 2000 to the middle of 2010. Fortunately, we have been slowly regaining manufacturing jobs since 2010 thanks to a great extent to the efforts of the Reshoring Initiative.
In April 2010, the Reshoring Initiative was founded by Harry Moser, retired president of GF AgieCharmilles LLC, a leading machine tool supplier in Lincolnshire, Illinois.to facilitate returning manufacturing to America from offshore by providing the right tool at the right time to with the creation of the Total Cost of OwnershipTM worksheet calculator spreadsheet. To help companies make better sourcing decisions, the Reshoring Initiative provides the Total Cost of OwnershipTM spreadsheet for free to help manufacturers calculate the real impact offshoring has on their bottom line. The website provides an online library of more than 7,000 articles about cases of successful reshoring.
The brief definition of TCO is an estimate of the direct and indirect costs related to the purchase of a part, sub-assembly, assembly, or product. However, a thorough TCO includes much more than the purchase price of the goods paid to the supplier. For the purchase of manufactured goods, it should also include all of the other factors associated with the purchase of the goods, such as: geographical location, transportation alternatives, inventory costs and control, quality control, as well as reserve capacity, responsiveness, and technological depth of the vendor.
Mr. Moser’s TCO spreadsheet includes calculations for the hidden costs of doing business offshore, such as Intellectual Property theft, danger of counterfeit parts, the risk factors of political instability, natural disasters, riots, strikes, technological depth and reserve capacity of suppliers, and currency fluctuation as well as effect on innovation, product liability risk, annual wage inflation, and currency appreciation.
Previous studies have shown that about 60% of companies made the decision to offshore based on comparing wage rates, FOB prices or landed costs, while ignoring the hidden costs and risk factors. Thanks to the Reshoring Initiative’s TCO worksheet, companies are becoming familiar with the broad range of factors they had previously ignored. The reasons that thousands of other companies have given for reshoring in the Reshoring Initiatives library of cases helps companies to determine whether those reasons are applicable to them.
According to the annual report released on December 7, 2020 by the Reshoring Initiative, “The projected job announcements for 2020 is 110,000, which will bring the total to over 1 million by year’s end…The combined reshoring and foreign direct investment (FDI) announcements in 2019 totaled more than 117,000 manufacturing jobs, plus an additional 24,800 in revisions to the years 2010 through 2018…Additionally, the number of companies reporting new reshoring and FDI was at the second highest annual level in history: 1,100 companies.”
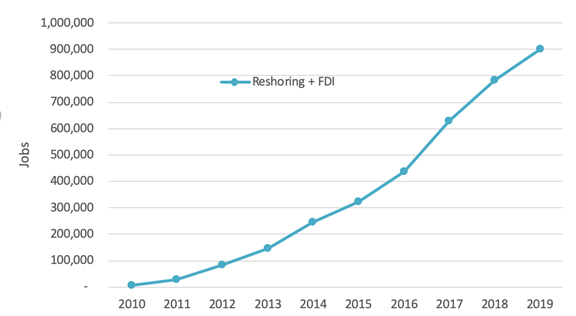
Jobs Announced, Reshoring and FDI, Cumulative 2010-2019
The report states: “Only products that have been offshored/imported can be reshored. Thus, the products least suitable for offshoring never left, such as heavy, high volume minerals, high mix/low volume items or customized automation systems.
The most active reshoring is by those that left and probably should not have done so, including machinery, transportation equipment and appliances. As the data indicates, reshoring is focused on products whose size and weight, e.g., transportation equipment, or frequency of design change/volatility of demand, e.g., some apparel, suggest that offshoring never offered great total cost savings.”
The term “FDI” means “Foreign Direct Investment” and refers to foreign companies that are investing in manufacturing plants in the U.S. to produce products closer to their major market of the U.S. Plants established by Japanese companies such as Toyota and Nissan, and plants established by German-owned BMW are examples of foreign investment.
However, we still have a long way to go as the report states: “When measured by our trade deficit of about $500 billion/year, there are still three to four million U.S. manufacturing jobs offshore at current levels of U.S. productivity, representing a huge potential for U.S. economic growth.”
The report states, “Companies have consistently reported Positive Factors more often than Negative, probably because the companies place more value on demonstrating the wisdom of their current reshoring decision than on what went wrong with their earlier offshoring decision. “
The top ten positive factors that influenced a reshoring decision are:
- Proximity to customers/market
- Government Incentives
- Eco-system synergies/Supply chin optimization
- Skilled workforce availability/training
- Image/brand
- Infrastructure
- Impact on domestic economy
- Lead time/time to market
- Automation Technology
- Customer responsiveness improvement
The top ten negative factors influencing the decision to reshore are:
- Quality/rework/warranty
- Freight cost
- Total Cost
- Delivery
- Rising Wages
- Inventory
- Supply chain interruption/Natural disaster risk/Political instability
- Green considerations
- Intellectual Property Risk
- Communications
The report states that the top industries that are reshoring or benefitting from FDI are:
- Transportation Equipment
- Computer & Electronic Products
- Electrical Equ8ipment, Appliances & Components
- Chemicals
- Plastic & Rubber Products
- Wood & Paper Products
- Apparel & Textiles
- Fabricated Metal Products
- Machinery
It’s not surprising that China ranks number one as the country from which companies are reshoring, with Mexico, Canada, India, and Japan filling out the top five. The top countries that are investing in manufacturing sites in the U.S. are: Germany, China, Japan, Canada, and Korea.
The authors note that “The South and Midwest continue to dominate cumulatively. The Midwest and Texas dominate reshoring and the South dominates FDI.” It was surprising to me that Michigan and New York were in the top five states for the number of jobs that were reshored, as they are not states where the cost of business is low. However, Texas ranked highest for both number of jobs announced and the highest number of companies reshoring.
The report authors state, “We believe the continued strength of the trends thru the end of 2019 is largely based on greater U.S. competitiveness due to corporate tax and regulatory cuts and increased recognition of the total cost of offshoring.”
It was interesting to note the impact of the COVID Pandemic on reshoring. The authors report: “The COVID Pandemic has increased in interest in reshoring as “Two in three (69%) manufacturing companies are looking into bringing production to North America (compared to 54% in February).”
In addition, “Repeated surveys show that more companies, driven by the virus crisis, have decided to reshore. We expect to see the data respond to this shift in 2021. Also due to the pandemic, we are seeing U.S. reshoring outpacing FDI for the first time since 2014…The national demand to shorten and close supply chain gaps for essential products to make the U.S. less vulnerable is most likely to benefit the following industries: PPE, medical, tech, and defense. Already, 60% of cases after March mention the pandemic as a factor in reshoring decisions. Medical equipment and PPE are the first responders of new reshoring with cases already double from last year.”
In conclusion, the authors state: “The revised rate of reshoring plus FDI job announcements in 2019 was up about 2000% from 2010. The 600,000+ jobs brought back represent about 5% of U.S. manufacturing employment. The acceleration of jobs coming back combined with the decline in the rate of offshoring has resulted in a plateauing of the goods trade deficit at about $800 billion/year. The COVID crisis has revealed the U.S.’s over-dependence on imports.
This data should motivate companies to further reevaluate their sourcing and siting decisions by considering all of the cost, risk and strategic impacts flowing from those decisions. Policy makers can use the continued reshoring successes as proof that it is feasible to bring millions of jobs back.”
Government policies do have an influence on reshoring and FDI. If the next administration reverses the corporate tax and regulatory cuts, it could have an adverse effect on the reshoring trend.