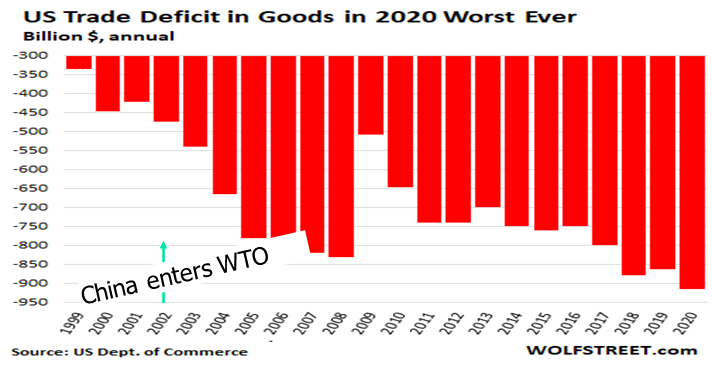
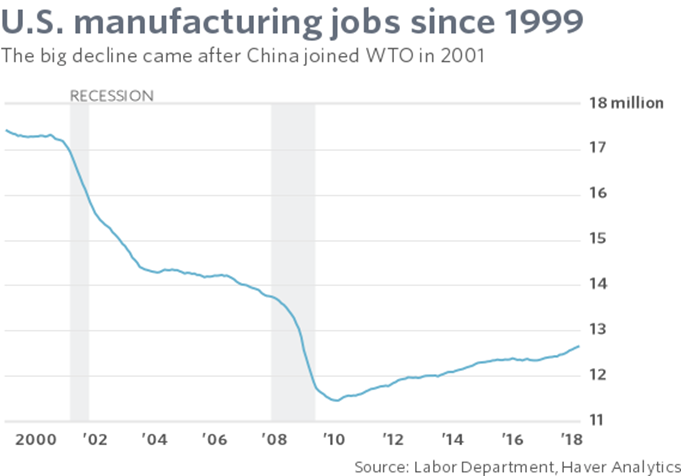
When I wrote the chapter on what manufacturers can do to save themselves for my first book, Can American Manufacturing be Saved? Why we should and how we can, published in 2009, one of my top recommendations was to begin the Lean journey to become a Lean manufacturer.
From 2006 – 2018, I benefited from attending monthly two-hour workshops offered by the Tech San Diego Operations Roundtable. Nearly all of these workshops focused on applying Lean methodologies and tools to manufacturing. San Diego was blessed with having several Lean experts put on these workshops, such as Steve Ebbing, Ric Van der Linden, Mike Osterling, and Jerry Wright.
In 2014, I met Luis Socconini, Founder and Director of the Lean Six Sigma Institute (LSSI), read his book, Lean Company, and took his Lean Six Sigma Yellow belt class 12 Saturdays in a row to earn my certificate.
Lean methodologies and tools to eliminate waste and improve productivity can enable a company to become a Lean manufacturer, but in his book, Mr. Socconini shows that there are processes in every critical activity within a company that can be made Lean, so that you can become a “Lean company.”
In his training, Mr. Socconini incorporates Lean accounting as “a very simple methodology to make it easy to calculate the real cost every week, every day, and even every hour. This makes it possible to make better decisions in real time and enables all the value stream leaders to understand if they are losing or wining.”
To get started on using Lean accounting, Mr. Socconini recommends that companies “need to select Lean accounting as one of the most important strategies for their business. Second, they need to implement calculating their “box score,” which is a tool to evaluate the financial results every week. Third, by using the box score, they will be able to calculate direct cost of products (normal material) and conversion cost (all the rest of the costs like energy, salaries, utilities, rent, etc. –everything but material or direct cost). With the conversion cost by hour, any company of any size or industry will be able to calculate real cost every day regardless of the mix or complexity. Real cost equals Conversion cost per unit plus material (direct cost).”
Mr. Socconini said, “The benefits of using Lean accounting compared to cost accounting are thata company is able to know what is the real cost and with this knowledge, they really know if the company is making money or losing money in real time. They are able to define correct prices for their products or services, decide which products or services are contributing profits and which of them are losers, prepare quotes with realistic information increasing the possibility of making better deals, and be able to define a target cost and compare it constantly with the real cost to drive the most important kaizen events.”
My appreciation of the importance of Lean accounting greatly increased when I had the pleasure of attending the Lean Accounting Summits five years in a row from 2014 – 2018 as a speaker representing the Reshoring Initiative on “Returning Manufacturing to American Using Total Cost of Analysis.”
These summits are produced by Lean Frontiers, headed up by founder and President, Jim Huntzinger. Each summit was two days of information-packed presentations and workshops that included case studies showing Lean principles and tools in action. The list of leading experts whom I met is too long to mention, and I would not want to leave someone out.
I share Jim Huntzinger’s belief that it is critical for accountants to be trained in Lean accounting and participate in the company transformation in order to have a sustainable company in the increasingly competitive global marketplace. Each year, Lean Frontiers provides scholarships to a few university and college professors to attend the conference to learn about Lean accounting.
One of the key points emphasized at each summit was “Utilizing Lean tools is not enough to become a Lean company. Lean concepts and principles must become part of the culture. Lean will not be sustainable in the long run unless it does.”
Within the San Diego region, I saw many companies that participated in the Operations Roundtable workshops I attended apply Lean principles and tools to transform into Lean manufacturers, but very few utilize Lean accounting outside of Mr. Socconini’s clients in the region.
The problem is that very few small companies of under 50 employees have begun to adopt Lean principles and tools, and in San Diego, 97% of all manufacturers have less than 50 employees. On a national level, “98.6% of American manufacturing companies are small businesses” (under 500 employees), and “75.3% of those businesses have fewer than 20 employees, according to data gathered by SCORE, mentors to America’s small businesses.”
The sad fact is that in recent conversations with over 20 Lean consultants around the country, there was a consensus that only about 5-7% of all manufacturers have transformed into Lean enterprises. These consultants agree that we need to find a way to make becoming a Lean enterprise less expensive, less time consuming, and easier to do to cross the chasm to the mainstream of small to medium companies
It’s a shame because small companies have the advantage of not having much of a hierarchy to flatten. However, in a small company, the president has to be fully committed to the Lean journey to initiate the training much less transform into a Lean enterprise.
Only two of the small manufacturers I have represented in the past 20 years have gone through Lean training. The first was a metal stamping company with less than 40 employees. They obtained the training through the College of the Canyons, one of the California Centers for Applied Competitive Technologies the offsets the cost with funding from California’s Employment Training Panel. As a result of the training, average throughput was reduced from five weeks to five days, on-time delivery improved by 70% and work-in-process was reduced by 40%. They did not adopt Lean Accounting and still had a problem with prices being higher than competition.
The other was Century Rubber Company with only 15 employees, and they received their training through the California Manufacturing Extension Partnership, California Manufacturing Technology Consulting. Their biggest benefit was eliminating wasted movement and time by implementing 5S, rearranging equipment, and reducing time to change molds. The cost of their training was also reduced by Employment Training Panel funding. Century utilizes a modified version of calculating conversion costs like Lean Accounting does, and their pricing became more competitive.
The companies I represent have sometimes lost orders for being two to four times higher than their Chinese competition, so I have a very good reason for encouraging a transition from standard cost accounting to Lean accounting. I firmly believe that if more companies would make this transition, we would be losing less business to China and other offshore suppliers.
Thirteen years and two books later, I have come to believe that any company that becomes a Lean enterprise will not need to offshore manufacturing to be globally competitive.
Therefore, I can’t stress enough the importance of your company beginning the Lean journey. I am certain that becoming a Lean Enterprise is one of the most important actions American manufacturers can take to be globally competitive and is one of the keys to rebuilding American manufacturing to create jobs and prosperity.