On July 22, 2019, the Coalition for a Prosperous America released an update to their study on the effects of increasing tariffs on all imported Chinese goods to 25% that had originally released in May. The study was conducted by CPA’s Chief Economist Jeff Ferry and Steven L. Byers, Ph.D. The Coalition for a Prosperous America is a non-profit, non-partisan organization working to eliminate the trade deficit with smart trade and tax policies to create jobs and prosperity.
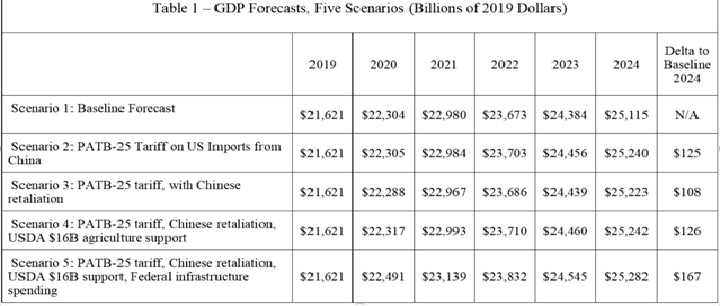
According to the report, “The tariff revenue totals $547 billion over five years. If those funds are reinjected back into the economy each year, this additional stimulus to growth results in a $167 billion boost to GDP and 1.05 million additional jobs in 2024…The results of the Coalition for a Prosperous America (CPA) model show that tariffs will have a sustained, positive impact on the US economy, including jobs, output, and investment.”
The report states: “The tariff would stimulate the US economy through two channels: first, the relocation of US-bound production from China to other nations would lead to a reduction in the average cost of imports because many alternative production locations ,such as those in Southeast Asia, today have lower costs of production than China; and secondly, because a portion of the production in China relocated to the US, would directly stimulate the US economy.”
In stark contrast, the opinions of professional economists are reflected in an article titled, “Trade Wars Are Not Good, or Easy to Win” in The Atlantic on August 5, 2019, staff writer Derek Thompson, wrote, ” President Donald Trump has stubbornly insisted on Chinese tariffs over the objections of his economic advisers—not to mention the near-universal outcry of the professional economic community. In a University of Chicago poll of several dozen international economists, zero disagreed with the statement that “the incidence of the latest round of US import tariffs is likely to fall primarily on American households.”
Why do the conclusions of the CPA research directors differ so greatly from the opinions of the economic community? The authors explained, “Our results differ remarkedly from other economic modeling efforts regarding tariffs…The differences result primarily from different assumptions about how businesses and consumers react to tariffs. Other models reflect a pro-free-trade bias and assume that (a) no production returns to the US as a result of tariffs (b )prices of US imports always rise when imports move from China to third countries and (c) US consumers react very negatively to higher prices, leading to educed sales and output in the US economy. A close study of the available empirical evidence shows these assumptions are unwarranted.”
The report states: “Our model consisted of two parts: a partial equilibrium model, which looked at how production in China for export to the US responded to the presence of a permanent across-the-board tariff, and a general-equilibrium model, based on the widely-used REMI economic model to explore the effects of production shifts on the US economy over a five-year forecast period.”
The report takes into consideration China’s retaliation against the tariffs and China’s moving manufacturing to the U.S. or other countries. It shows that the tariffs will encourage production relocation out of Asia and generate significant reshoring of manufacturing to the US by American manufacturers who had established plants in China. This opinion concurs with the data collected by the Reshoring Initiative for several year showing that “the location decision for manufacturers is not just about cost: reliable supply, closeness to customers, political stability, and building customer/consumer brand awareness all matter!”
The original May report went into more detail about the benefit of reshoring, stating, “The US job gains from PATB-25-induced reshoring are disproportionately concentrated in the manufacturing sector, with 192,416 additional manufacturing jobs (27 percent of total jobs created by the tariff). This is because the vast majority of US imports from China are manufactured goods. By 2024, our model forecasts that $69 billion worth of annual production will have migrated from China to the United States. While US production costs in many industries remain higher than in China, that is not the whole story. Locating production in the US offers other advantages, including lower transportation costs, more logistical flexibility, and closer connectedness to consumer markets, distributors, and senior management. Relocating in the US also insulates companies against the uncertainty of potential future trade tensions. Some industries, such as apparel, have already seen reshoring due to these advantages. A permanent tariff would speed up the process.”
In a webinar to CPA members on August 1st, Ferry cited several examples of American companies reshoring production to the US; namely, Caterpillar, Stanley Black and Decker, Hasbro, Whirlpool, Optec, and West Elm. The website of the Reshoring Initiative lists nearly 3,000 companies that have reshored, and the list grows by the week.
In an interview for The Epoch Times, Ferry said: “As time goes by, people are accepting it because they’re seeing that tariffs are not provoking huge increases or any increases in consumer prices. They’re not disrupting our supply chains”
He also said “the goal of the U.S. government is to fix these problems and to restore prosperity to the United States, and he thinks tariffs have their role to play. If the trade deficit continues, and if we want to see certain manufacturing industries grow in the United States, I think we need to do more, and tariffs on all Chinese imports is a good solution…It’s a delicate and dangerous game [the Chinese regime is] going to have to play to pivot from being an economy that’s completely dependent on exports to being a more balanced economy, and it’s anybody’s guess whether they can pull it off.”
I’m betting that the conclusions reached by CPA would prove true if President Trump did impose 25% tariffs on all imports from China because of the strong evidence of the benefit of reshoring to the US economy. According to the Reshoring Initiative, data from the manufacturing employment low of January 20190 through 2018, 749,000 jobs have been brought back to the US from offshore. In addition, manufacturing jobs pay higher than service and retail jobs, so tax revenue will increase from more people having higher paying jobs. Another benefit would be that as we reduce our imports, our trade deficit would go down. However, the best benefit is that as we resume making the products and systems needed to defend our country in the US, we will protect our national security.