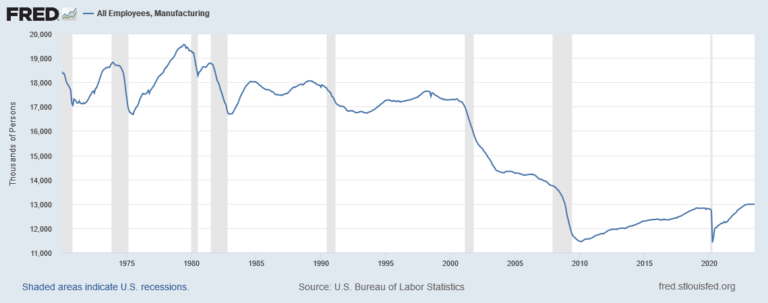
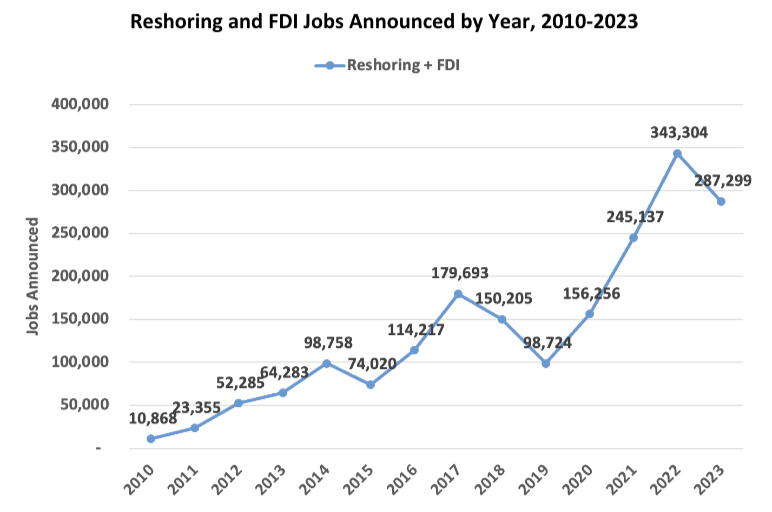
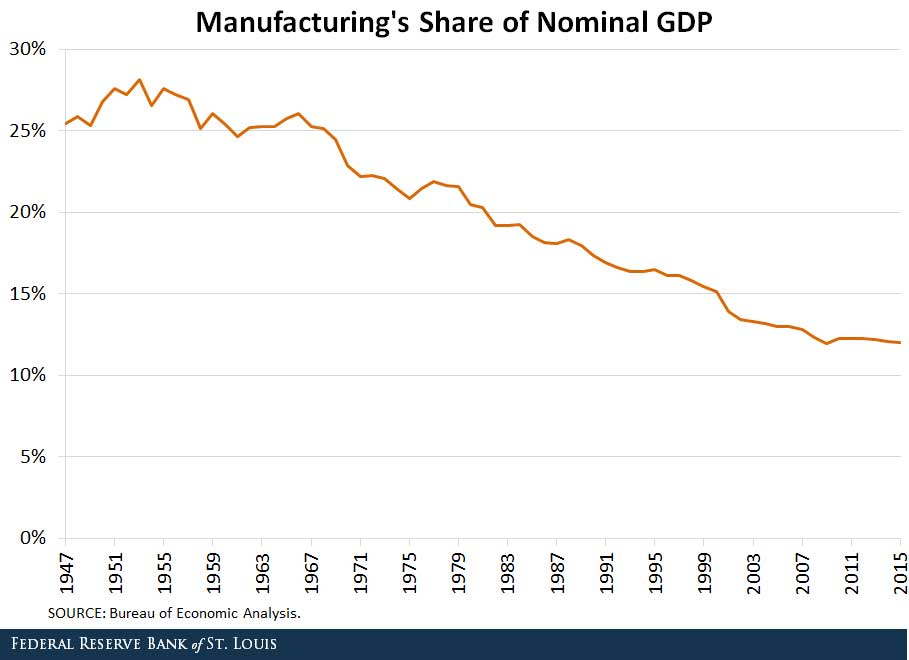
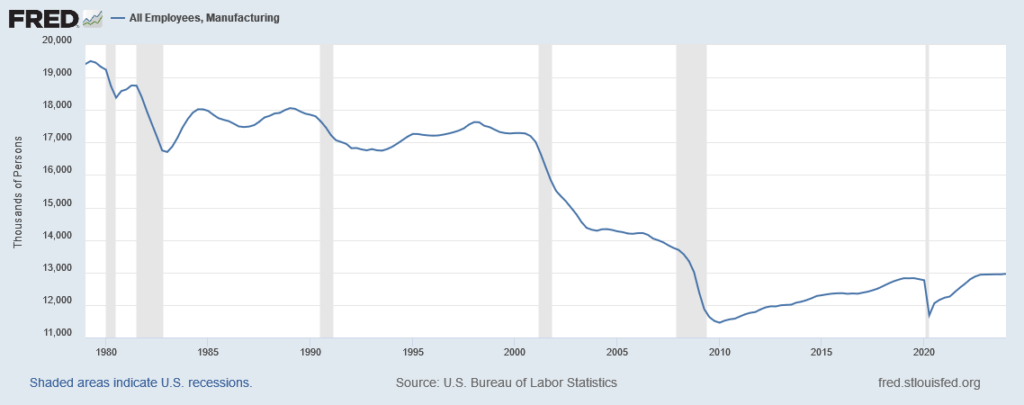
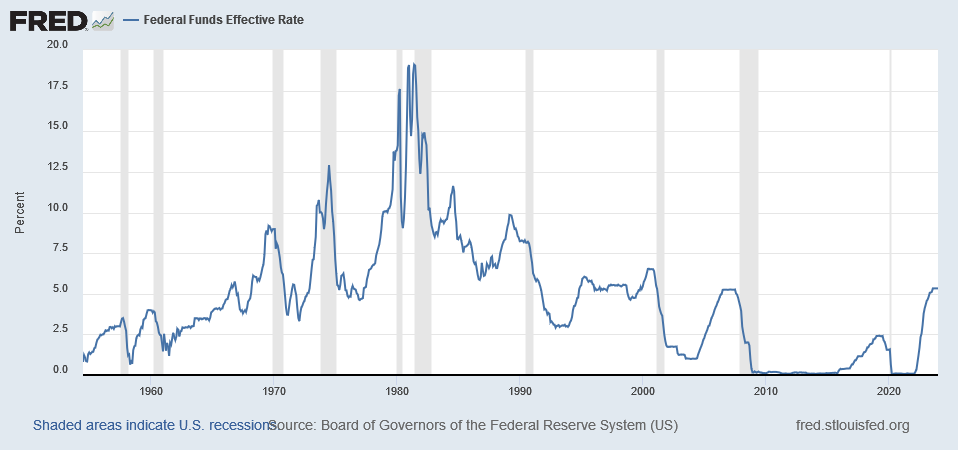
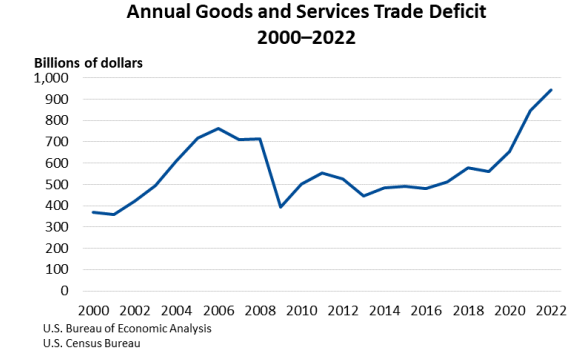
On March 12, 2025, President Trump “imposed sweeping 25% tariffs on all steel and aluminum imported into the United States…” causing some economists to warn “that broad-based tariffs threaten to drive up prices on everything from food to new homes.” In answering the question of whether tariffs would increase inflation, we can consider whether or not inflation was increased by the imposition of Section 232 tariffs on steel and aluminum and the 301 tariffs levied on roughly half of U.S. imports from China, and we can consider the benefits achieved from these tariffs in 2018.
Tariffs have traditionally had a two-fold purpose: protect American manufacturers from unfair trade practices by mercantilist countries and stimulate domestic production. The Section 232 and 301 tariffs were aimed to protect the domestic steel and aluminum industries from what the government perceived as unfair competition and national security threats. Here are some benefits that were projected from these tariffs:
Section 232 Tariffs:
- Protection of Domestic Industries: By imposing tariffs on imported steel and aluminum, the U.S. government intended to protect and support domestic producers of these metals.
- Stimulating Job Growth: The tariffs were expected to create and maintain jobs in the U.S. steel and aluminum industries by making imported metals relatively more expensive compared to domestic products.
- Infrastructure Development: With a healthier domestic steel and aluminum industry, there was an expectation of increased capacity and capability to supply materials for critical infrastructure projects across the country.
Section 301 Tariffs:
- Addressing Intellectual Property Concerns: The Section 301 tariffs targeted imports from China and were aimed at addressing intellectual property theft and unfair trade practices in various industries, including steel and aluminum.
- Leveling the Playing Field: By imposing tariffs on Chinese goods, the U.S. sought to level the playing field for domestic steel and aluminum producers who may have been competing against subsidized Chinese products.
- Encouraging Fair Trade Practices: The tariffs were intended to push China towards adopting fair trade practices and addressing concerns related to market access, technology transfer, and intellectual property rights.
Here are some specific examples of how the Section 232 and 301 tariffs have benefited the U.S. steel and aluminum industries:
- Expanding Existing Plants:
- Example: Nucor Corporation, a leading steel producer in the U.S., announced plans to invest $1.35 billion to build a new steel plate mill in Kentucky after the implementation of tariffs on steel imports under Section 232. This expansion will not only create more jobs but also increase production capacity, catering to the rising demand for steel products in the country.
- Building New Plants:
- Example: Alcoa, a prominent aluminum producer, decided to restart its aluminum smelter in Evansville, Indiana, following the tariffs imposed on aluminum imports under Section 232. This move signifies a significant investment in building a new plant that will contribute to the growth of the domestic aluminum industry, providing employment opportunities and supporting the local economy.
- Adding Employees:
- Example: U.S. Steel Corporation hired additional employees at its plant in Granite City, Illinois, in response to the tariffs imposed under Section 232. The increased demand for domestic steel prompted the company to bring back workers who were previously laid off and also recruit new talent to support the plant’s operations, showcasing the positive impact of tariffs on job creation within the industry.
Overall, the Section 232 and 301 tariffs have played a crucial role in revitalizing the U.S. steel and aluminum industries by encouraging investments in plant expansions, new construction projects, and workforce expansion, thereby fostering growth and competitiveness in these sectors.
Now, let’s examine whether or not these tariffs increased inflation since going into effect in 2018. The U.S. International Trade Commission (USITC) released the report, Economic Impact of the Section 232 and 301 Tariffs on U.S. Industries in March 2023. “It took an in-depth look at the effects of these tariffs on the importing industries and on industries dependent on them…over the years 2019 through 2021. In every one of the ten industries the authors studied, the 301 tariffs led to significant increases in domestic production.” An article titled “USITC Report Shows Tariffs Boosted U.S. Production” by Jeff Ferry, Chief Economist of the Coalition for a Prosperous America, states that the key points of the report were:
- “Section 301 and 232 tariffs boosted production in all twelve of the industries studied.
- Price increases in the product categories targeted with tariffs were very small, in the 3%-4% range, contrary to mainstream media narrative.
- Most of the tariffs targeted intermediate (industrial) goods. Downstream goods, including consumer goods, saw barely visible tariff-related price increases.
- Downstream price increases due to steel and aluminum tariffs were estimated to be 0.2%.
- Section 232 steel tariffs unleashed a huge wave of steel investment, likely creating some 20,000 direct jobs.
- Tariffs are a valuable tool for generating growth in the U.S. economy.”
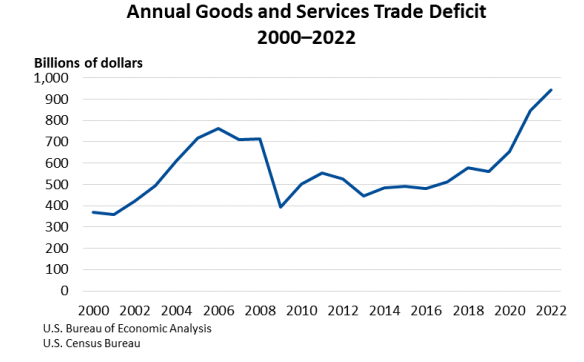
Since these tariffs were beneficial for the steel and aluminum industries, additional tariffs would be beneficial to other American manufacturing industries and help reduce our increasing trade deficits.
The Press Release on March 19, 2025 by the Coalition for Prosperous America titled: “Importers Front-Run Global Tariffs; Deficit Expands a Record Breaking 34% in January” by Kenneth Rapoza states:
“January imports rose 10% to $401.2 billion while exports rose at their usual pace, around 1% to $269.8 billion, according to the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA)…The January goods deficit is the biggest in years, if not ever.”
The top 10 deficit countries as measured inbillions of dollars were: “China ($29.7), the European Union ($25.5), Switzerland ($22.8), Mexico ($15.5), Ireland ($12.4), Vietnam ($11.9), Canada ($11.3), Germany ($7.6), Taiwan ($7.5) and Japan ($7.4).”
These high trade deficits explain why President Trump is proposing 25% tariffs on imports from China, Canada, and Mexico.
On March 19, 2025, the Coalition for a Prosperous America released a memorandum titled “CPA Recommendations for Implementing Tariffs Pursuant to the America First Trade Policy” by Charles Benoit as a response to the Presidential Memorandum titled America First Trade Policy President Trump issued on his Inauguration Day.
It states: “CPA is strongly supportive of President Trump’s Trade and Tariff Agenda that seeks to broadly reindustrialize the United States and raise significant revenue as outlined in the America First Trade Policy Memorandum.”
“However, CPA cautions against adopting a reciprocal tariff strategy aimed primarily at negotiating lower foreign trade barriers and more favorable investment conditions abroad. A reciprocal tariff strategy that prioritizes foreign governments’ willingness to reduce their trade barriers or be more receptive to foreign investment is in conflict with the stated goals of the America First Trade Policy Memorandum and undermines the predictability and stability American businesses need to confidently invest in long-term domestic production.”
CPA offers the following recommendations as they relate to the use of tariffs for protection, for revenue, and for reciprocity.
Tariffs for Revenue:
- CPA fully supports President Trump’s concept of a 10% to 20% supplemental, universal tariff. CPA estimates that even a modest 10% supplemental universal tariff would lead to $728 billion in economic growth and 2.8 million new jobs, while generating $263 billion in new federal revenue to pay for domestic tax cuts.
Tariffs for Protection:
- Section 232 is an excellent Presidential tool for protecting American producers, and CPA applauds the Trump Administration for already initiating new Section 232 investigations on copper and lumber.
- CPA believes it is essential that entire supply chains be considered for the successful deployment of tariffs. Conveniently, Sections I through XX (1 through 20) of the Harmonized Tariff System (HTS) are organized in this way. The Trump Administration should consider initiating a Section 232 review for each of Sections 1 through 20 of the HTS.
Tariffs for Reciprocity
Reciprocal tariffshaven’t worked to the benefit of the United States ever since the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) went into effect in 1948. When the World Trade Organization was established in 1995, “every WTO Member, including the United States, has pledged maximum tariff rates applicable to every other WTO member…Under the WTO system, there’s no single maximum rate, but rather specific maximum rates — known as ‘bound rates’ — itemized across 5,000+ product categories. Bound rates for each WTO country are listed in that country’s ‘Schedules of Concessions,’ which is annexed to the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT.)”
Supposedly level tariff rates haven’t prevented the United States from incurring an ever-increasing trade deficit with its trading partners because of mercantilist practices such as undervalued currency, subsidies to the manufacturing industries of the respective countries, intellectual property theft, and product dumping, among other practices. Thus, CPA concludes: “These reciprocity requirements have all failed while simultaneously pitting American producers against each other.”
Instead,” CPA calls on the Trump Administration to either withdraw from the World Trade Organization entirely, or to “Unbound” the United States’ Schedule of Concessions to the GATT.”
The Trade and Tariffs page of the CPA website states, “The Coalition for a Prosperous America (CPA) has proposed a model that uses a simple, four-level structure of global tariffs at 0%, 15%, 35% and 55% (explained more in the document). CPA projects that this tariff would create 10 million new producer jobs, increasing real household incomes by 10%, grow the economy by 7% and generate $603 billion in new revenue. This revenue is more than sufficient to eliminate income taxes on the large majority of American wage earners.
The economic benefits of imposing tariffs on all imported goods can be summarized to be:
- Protection of domestic industries: Tariffs can protect domestic industries from foreign competition by making imported goods more expensive. This can help prevent job losses in sectors that are unable to compete with cheaper imports.
- Revenue generation: Tariffs can generate revenue for the government. The revenue collected from tariffs can be used to fund government programs, infrastructure projects, or reduce budget deficits.
- Trade balance improvement: By making imported goods more expensive, tariffs can help reduce imports and improve the trade balance of the country. This can help decrease trade deficits and strengthen the economy.
- Encouraging domestic production: Higher tariffs can incentivize businesses to produce goods domestically rather than importing them. This can lead to increased investment in domestic production facilities and create jobs.
- National security: Imposing tariffs on certain imported goods can also be used as a strategic tool to protect industries that are deemed critical to national security.
In my opinion, these benefits make tariffs an attractive alternative to the free-trade policies that have dominated the past 70 years of international trade. Protecting and encouraging more domestic production would increase manufacturing’s share of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and improve the financial wellbeing of many more Americans.