On October 16th, about 130 business leaders met at the conference facilities of AMN Healthcare in San Diego for the third “Manufacturing in the Golden State – Making California Thrive” economic summit. The summit was hosted by State Senator Mark Wyland in partnership with the Coalition for a Prosperous America and a long list of other regional businesses and associations. The purpose of the summit was to discuss how several national and California policies are threatening the growth and prosperity of California manufacturers and what policies should be changed to help them grow and thrive.
After State Senator Wyland welcomed attendees, Michael Stumo, CEO of the Coalition for a Prosperous America, provided an overview of the schedule for the day.
I provided an update to the overview of California manufacturing that I had presented at our summit in Brea on March19th covered in a previous article. California lost 33.3% of manufacturing jobs between 2000 and 2009 compared to 29.8% nationwide and 25% of its manufacturing companies. California lags in manufacturing job growth at a .36% rate compared to the national 6.09% rate.
I highlighted that the San Diego region offers a great deal of help for inventors and start-up technology based companies through the San Diego Inventors Forum, CONNECT’s Springboard program, the Small Business Development Centers in North County and South County, CleanTech San Diego, as well as groups like the San Diego Sports Innovators. San Diego also offers more career path and workforce training programs than most other states, including those offered by three of our event sponsors: California Manufacturing Technology Consulting, the Center for Applied Competitive Technologies, and the Lean Six Sigma Institute.
The good news is that California is benefitting from the reshoring trend that is sweeping the county. According to data collected by the Reshoring Initiative, California ranks first in the number of companies (28) that have reshored and third in the number of jobs created by reshoring (6,014).
I then moderated a panel of the following local manufacturers, who gave their viewpoints of the effects of some of our national policies and the challenges of doing business in California:
- James Hedgecock, Founder and General Manager of Bounce Composites
- Scott Martin, President, Lyon Technologies
- Robert Reyes, Head of Strategic Sourcing, Stone Brewing Company
Hedgecock stated that Bounce Composites is less than two years old and makes thermoset composites, starting with paddle boards and branching into small wind turbine blades this year. He bemoaned the fact that in California you have to pay $800 to incorporate a company, which is double to quintuple the cost of incorporating in other states. Also, as a LLC, you have to pay taxes on gross profits rather than net profits, which is tough on a start-up company.
Martin said that Lyon Technologies has been in business since 1915 and has changed its products several times over the years. Current products include bird and reptile incubators, poultry products, and veterinary products, which they export to about 100 countries. He stated that the Value Added Taxes (VATs) that are added to the products they export and the currency manipulation practiced by several countries make it difficult for their products to be competitive in the world marketplace.
Reyes said they are expanding out of San Diego and are building a new $25M brewery and restaurant in the Marienpark Berlin, scheduled to open by end 2015/beginning 2016. Stone exports beer to Germany and other European countries and having a brewery in Germany will ave on shipping costs for exporting. They are also planning on opening a brewery on the East Coast in Virgina.
The national expert panel included Greg Autry, Adjunct Professor of Entrepreneurship, Marshall School of Business, University of Southern California; Pat Choate, economist and author, “Saving Capitalism: Keeping America Strong”; Mike Dolan, Legislative Rep., International Brotherhood of Teamsters; and Michael Stumo, CEO of CPA. The focus of the talks was on national security, manufacturing growth strategies, tax strategies and fixing the trade deficit.
Autry, led off the national panel with the topic of “National Security Concerns with U. S. Trade Regime.” He began by stating, “An economy that builds only F-35s is unsustainable – productive capacity is what wins real wars. Sophisticated systems require complex supply chains of supporting industries. They require experienced production engineers and experienced machinists.” He added that we cannot rely on China to produce what we need for our military and defense systems. “We should not be relying on Russia’s Mr. Putin to launch our satellites and space vehicles and provide us a seat to get to the international space station.”
He pointed out that our technical superiority in military systems will not assure our national security any more than the technical superiority of Nazi Germany’s aircraft and tanks did for them. Economic superiority is what matters. The manufacturing industry of the U. S. out produced Germany during WWII and the Soviet Union in the Cold War.
Autry stated that Wall Street’s new hero, Jack Ma, founder of Chinese company Alibaba Group Holding Ltd, is a danger to American interests by the fact that Alibaba just overtook Amazon as the world’s largest online retailer by market capitalization. It was the wealth he created at Amazon that enabled founder Jeff Bezos to now lead a new company, Blue Origin, which was just selected by the United Launch Alliance to finish development of a new engine to replace the Russian made RD-180 rocket engine used by ULA’s Atlas 5 rocket. There is considerable skepticism by many of Mr. Ma’s independence from the Chinese government. Mr. Ma’s next target appears to be PayPal, which is responsible for the wealth of Elon Musk, now CEO and CTO of SpaceX, CEO and chief product architect of Tesla Motors, and chairman of SolarCity.
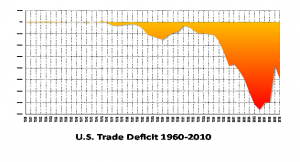
Next, Michael Stumo presented “A Competitiveness Strategy for America: Balance Trade and Rebuild Domestic Supply Chains.” He said, “Our ultimate goals should be: improved standard of living, full employment, and durable, sustainable growth. America has no strategy to win. Our trade deficit cuts our growth in half. Domestic supply chains were sacrificed to global supply chains; i.e. offshored and hollowed out….We need a strategy to win.”
He pointed out that “free trade is supposed to produce balance and address foreign mercantilism, but our trade policies enable mercantilism…We must replace the goal of ‘eliminating trade barriers’ and have Congress establish a new directive via statue to balance trade.”
He said that to achieve balanced trade, we must address, reciprocity, currency manipulation, forced technology transfer [by China], foreign VAT rebates, state-owned enterprises, and government subsidies.
In conclusion, he recommended that we should:
- Create durable comparative advantage through technical superiority, infrastructure, low energy costs, etc.
- Balance trade and fight foreign mercantilism
- Create our own comparative advantage
- Maximize domestic value added
- Identify and minimize our advantages while minimizing our disadvantages
In conclusion, he urged, “Don’t be afraid of asserting and pursing our national economic interest.”
The next speaker was Mike Dolan, Legislative Representative for the Teamsters, who has long experience working for Fair Trade (fighting expansion of the job-killing NAFTA/WTO model). He said that big corporations want Congress to pass Trade Promotion Authority in the “lame duck” session to grant the president Fast track Authority for the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) and the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) Agreements. He called the TPP “NAFTA on steroids” and said that TTIP is just as bad. He said that Fast Track was invented by President Nixon and has been used 16 times. He said that we need a new form a Trade Promotion Authority where Congress has input with regard to the countries involved in the Agreement, certifies that negotiating goals were met, and votes to approve it before it is signed. He urged attendees to contact their Congressional Representative to oppose the TPP for the following reasons:
- “Lack of transparency during negotiations warrants more thorough consideration than a up or down vote
- Under previous trade deals, the U. S. has hemorrhaged jobs and cannot afford more of the same
- The TPP is too large and complex to delegate constitutional authority away from Congress”
Pat Choate (Economist; Author, Saving Capitalism: Keeping America Strong) discussed how our trading partners have used Value Added Taxes (VATs), and currency manipulation to their advantage and to the disadvantage of the U. S. VATs or border adjustable consumption taxes are used by other countries to offset income, payroll, or other employer taxes to help their manufacturers be more competitive in the global marketplace or to offset other costs like national health care or pension programs. VATs range from a low of 10% to a high of 24%, for an average of 17%.
While tariffs have been dropped since 1968 as part of many trade agreements signed since then, the effective trade barriers have remained constant because of the VATs being imposed.
These consumption taxes have been a causative factor in increasing our trade deficits with our trading partners, which was $471.5 billion in 2013, $318 billion with China alone. He supports CPA’s advocacy of making changes in U. S. trade policy to address this unfairness which tremendously distorts trade flows.
During lunch, keynote speaker Dan DiMicco, Chairman Emeritus of Nucor Steel Corporation, spoke on “Seizing the Opportunity.” He led off by shocking the audience with facts about the real state of our economy and our unemployment rate. By September 2014, we still had not reached the level of employment that we had when the recession began in December 2007 although 81 months had passed. We lost 8.7 million jobs from December 2007 to the “trough” reached in February 2010, but because our recovery has been much slower than the previous recessions of 1974, 1981, 1990, and 2001, the gap in recovery of jobs compared to these recessions is actually 12,363 jobs.
In contrast to the misleading U-3 unemployment rate of 5.9% for September 2014 that is reported in the news media, the U-6 rate was 11.8%. The government’s U-6 rate is more accurate because it counts “marginally attached workers and those working part-time for economic reasons.”However, the actual unemployment is worse because the participation in the workforce has dropped from 66.0% to 62.7%. In other words, if the December 2013 Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate was back to the December 2007 level of 66.0%, it would add 8.2 million people to the ranks of those looking for jobs.The manufacturing industry lost 20% of its jobs, and the construction industry lost 19% of its jobs.
Unemployment Data Adjusted For Decline in Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate
(Adjusted For Decline from December 2007 Level Of 66.0% to 62.8% in September 2014)
| Reported Unemployed U.S. Workers | 9,262,000 |
| Involuntary Part-time workers | 7,103,000 |
| Marginally Attached To Labor Force Workers | 2,226,000 |
| Additional Unemployed Workers With 66% CLF Participation Rate | 8,199,000 |
| Unemployed U.S. Workers In Reality | 26,770,000 |
| Adjusted Civilian Labor force | 166,287,000 |
| Unemployment Rate In Reality | 16.1% |
DiMicco said, “We got in this position from 1970 until today because of failed trade policies allowing mercantilism to win out against true FREE Trade. We bought into wrongheaded economic opinions that America could become a service-based economy to replace a manufacturing-based economy. Manufacturing supply chains are the Wealth Creation Engine of our economy and the driver for a healthy and growing middle class! The result has been that manufacturing shrank from over 30% to 9.9% of GDP causing the destruction of the middle class. It created the service/financial based Bubble Economy (Dot.com/Enron/Housing/PONZI scheme type financial instruments.)”
He added, “We have had 30 years of massive increases in inefficient and unnecessary Government regulations. These regulations, for the most part, in the past have been put in place by Congress and the Executive Branch. However, today they are increasingly being put in place by unelected officials/bureaucrats as they intentionally by-pass Congress.
American’s prosperity in the 20th century arose from producing more than it consumed, saving more than it spent, and keeping deficits to manageable and sustainable levels. Today, America’s trade and budget deficits are on track to reach record levels threatening our prosperity and our future.”
He said, “Creating jobs must be our top priority, and we need to create 26-29 million jobs over the next 4-5 years. There are four steps we can take to bring about job creation:
- Achieve energy independence.
- Balance our trade deficit.
- Rebuild our infrastructure for this century.
- Rework American’s regulatory nightmare.
In conclusion, DiMicco said, “We need to recapture American independence through investment in our country’s people, infrastructure, and energy independence, and by reversing the deficit-driven trends that currently define our nation’s economic policy. Real and lasting wealth IS, and always has been, created by innovating, making and building things — ALL 3 ? and servicing the goods producing sector NOT by a predominance of servicing services!”
As the mid-term election approaches, we need to cast our votes for candidates who address the serious issues discussed at the summit, so that we can work together as Americans to restore California to the Golden State it once was and restore America to be “a shining city upon a hill whose beacon light guides freedom-loving people everywhere,” as declared by Ronald Reagan in 1974.