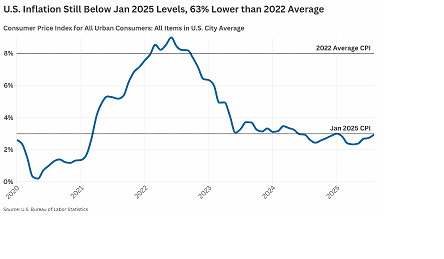
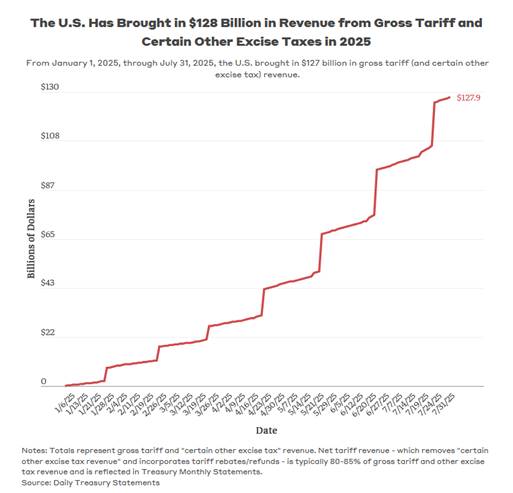
should pass that fulfills their campaign promise to support President’s Trump goal to Make America Great Again and help rebuild American manufacturing. This article will examine whether or not Congress passed any of the legislation I recommended.
Impose a Market Access Charge (MAC) as proposed by Dr. John R Hansen, (PhD economist and Economic Advisor, The World Bank (retd.) “forcing foreigners to pay a market access charge (MAC) on inflows of all foreign-source money.”
The answer is still “no” as revealed in my article, “Why a Market Access Charge Would Have Greater Benefits Than Tariffs,” dated December 12, 2025. The passage of such a bill would address the problem of the U.S. dollar competing against the undervalued currencies of China, Vietnam, Korea, and Japan. It would moderate the gross inflows of “trash cash” into the speculative financial market of stocks and bonds and help American products be more competitive in the global marketplace, which would grow our manufacturing industry and create more higher paying jobs.
Pass a Patent Reform Bill to restore inventors’ rights and end abuses by the Patent Trial and Appeal Board (PTAB).
As revealed in my November 18, 2025 article, “Legislation Protecting Inventors’ Rights Reintroduced to Congress,” the answer is “yes” as the Restoring America’s Leadership in Innovation Act (RALIA) (H.R. 5811) was introduced in the 119th Congress by Rep. Thomas Massie (R-KY) with Rep. Marcy Kaptur (D-OH) as a key co-lead, with its text filed on October 24, 2025, aiming to overhaul U.S. patent law, including abolishing the PTAB and restoring “first to invent” standards.
Revoke China’s Most Favored Nation Status (aka Permanent Normal Trade Relations (PNTR)
The answer is “no.” The 119th Congress has not yet revoked China’s Permanent Normal Trade Relations (PNTR), but several bipartisan bills have been introduced: H.R. 694, The Restoring Trade Fairness Act, introduced on January 23, 2025 by Rep. John Molenaar (R-MI) and S. 206, The Restoring Trade Fairness Act, introduced by Sen. Tom Cotton (R-AR) on January 23, 2025.
These bills represent a bipartisan effort to end China’s PNTR, applying Column 2 tariff rates (minimum 35%, strategic goods 100%) and eliminating duty-free de minimis treatment on small shipments. These bills are stalled in their respective committees in the House and Senate.
Reduce the Allowed Value of De Minimis imports
No, Congress hasn’t enacted legislation, but a White House Fact Sheet states that on April 2, 2025, “President Trump is ending duty-free de minimis treatment for covered goods from the People’s Republic of China (PRC) and Hong Kong starting May 2, 2025.”
“All relevant postal items containing goods that are sent through the international postal network that are valued at or under $800 and that would otherwise qualify for the de minimis exemption are subject to a duty rate of either 30% of their value or $25 per item (increasing to $50 per item after June 1, 2025).”
Them, on July 31, 2025, President Trump signed an executive order suspending duty-free de minimis treatment for low-value shipments. “Effective August 29, imported goods sent through means other than the international postal network that are valued at or under $800 and that would otherwise qualify for the de minimis exemption will be subject to all applicable duties.”
Executive Orders may be revoked by subsequent presidents, so it is important that Congress passes legislation to permanently suspend duty-free de minimis treatment for low-value shipments.
Both : H.R. 694 the Restoring Trade Fairness Act and S. 206 The Restoring Trade Fairness Act, mentioned above would permanently suspend duty-free de minimis treatment for low-value shipments in addition to revoking China’s PNTR status. It is important that these bills be approved by their committees to be voted on by the House and Senate.
Reauthorize a Reformed Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA)
The answer is “yes”. The Bloomberg Government newsletter of September 30, 2025, states “The One Big Beautiful Bill Act (OBBBA), P.L. 119-21, makes permanent key provisions of the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, including lower individual tax rates, enhanced deductions, a higher estate and gift tax exemption, and the 20% pass-through deduction. Business tax breaks for research and development, property depreciation, and interest expenses are also now permanent…the state and local tax (SALT) deduction cap rises to $40,000 for five years, then reverts to the $10,000 cap… The OBBBA also fulfills several campaign-trail promises with short-term measures, many set to expire after 2028 to limit their cost. These include new deductions for tips, overtime pay, and car loan interest on American-made vehicles, and an additional $6,000 deduction for individuals aged 65 and older.”
The manufacturing industry will also benefit from some of the other provisions of the OBBBA:
- Authorizes sizable investments in technology and infrastructure
- Automakers no longer face civil penalties for violations of fleetwide fuel economy standards issued by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
- Increases the advanced manufacturing tax credit, including for chipmakers, from 25% to 35%.
- Restores the Federal Communications Commission’s authority (lapsed in 2023) to auction spectrum licenses through 2034
- Authorizes $1 billion to fund the Defense Production Act
- Prioritizes fossil fuel development, while renewable energy programs are to be phased out
- Expands drilling on public land, including four onshore lease sales in nine western states, broader access to all leasable lands, and an extension of drilling permits to four years (up from three)
- Mandates offshore lease sales in the renamed “Gulf of America,” Alaska’s Cook Inlet, the National Petroleum Reserve–Alaska, and the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge
- Directs the Interior Department to approve qualified coal leasing applications, offer 4 million acres for coal leasing, and increase annual federal timber sales through 2034
- Lowers royalty rates on oil, gas, and coal; eliminates royalties on extracted methane; and ends fees for nominating parcels for leasing
Pass Legislation to Address China’s Exploitation of U.S. Capital Markets, Economic Incentives, and Trade Policy
Congress is actively considering the following bills to counter China’s economic influence, targeting capital markets, trade, and technology:
The FIGHT China Act of 2025 (S.1053) was introduced in the Senate by Sen. John Cornyn (R-TX) on March 13, 2025. A sister bill (H.R.3946) was introduced in in the House introduced by Rep. Andy Barr (R-KY). The FIGHT China Act restricts American investment into Chinese Communist Party (CCP) military and surveillance companies and other sensitive technologies of adversarial nations. The December 17, 2025 press release by Rep. Barr states: “Today, the FIGHT China Act led by U.S. Congressman Andy Barr (R-KY) and U.S. Senator John Cornyn (R-TX) passed the U.S. Senate…The legislation is the strongest sanctions ever passed by Congress on China…This legislation will make President Donald J. Trump’s America First Investment Policy permanent and prevent American investors from unknowingly bankrolling military and tech companies that threaten U.S. national security.” Instead of being signed by President Trump as a separate bill, it was added to the 2026 National Defense Authorization Bill mentioned below.
The SAFE Act, Secure America’s Financial Exchanges Act (S.1357) has five co-sponsors in the Senate: Rick Scott (R), Marsha Blackburn (R), Bill Cassidy (R), Cindy Hyde-Smith (R), and John Neely Kennedy (R). It “would amend the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 to address the issuance of securities by Chinese entities… would require Chinese companies seeking to list securities on U.S. exchanges to disclose detailed information about their relationship with the Chinese government. Specifically, companies would need to reveal any financial support received from the People’s Republic of China, including subsidies, loans, tax benefits, or procurement policy advantages. They must also describe the conditions attached to such support, such as requirements to meet export targets, purchase from specific entities, use certain intellectual property, or employ Chinese Communist Party members. Additionally, companies would have to disclose the presence and composition of Chinese Communist Party committees within their organization, and provide background on any officers or directors who currently or previously held positions in the Chinese government or Communist Party.”
The TASK Act, Transaction and Sourcing Knowledge Act (S.1358), introduced by Senator Rick Scott on April 8, 2025, aims “to enhance transparency by requiring public companies to report on supply chain due diligence, particularly concerning forced labor in Xinjiang, China, to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), bolstering investor protection and addressing human rights concerns through mandated disclosure.”
However, there was another bill that became law in late December that has provisions that benefit American manufacturers and helps rebuild American manufacturing. This is S.1071 – National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2026, which includes significant provisions to benefit American manufacturers by boosting domestic production, funding advanced technologies, creating new networks like the Civil Reserve Manufacturing Network, and focusing on key areas like semiconductors, shipbuilding, and munitions to strengthen the defense industrial base (DIB). Key measures are:
- Defense Industrial Base Fund Expansion: Broadens allowable spending for materials, equipment, facility construction, and advanced manufacturing investments within the DIB.
- Civil Reserve Manufacturing Network (CRMN): Establishes a system to rapidly qualify commercial factories to produce defense items during emergencies, increasing surge capacity.
- Advanced Manufacturing & Technology:
- Funds R&D for next-gen tech and mandates DoD to adopt advanced methods like additive manufacturing (3D printing).
- Elevates advanced manufacturing in acquisition governance, co-chairing key groups.
- Supply Chain Resiliency: Focuses on domestic production for critical items like semiconductors and aims to build advanced manufacturing facilities in the Pacific.
- Workforce & Skills: Supports upskilling workers and creating pathways for military skills to translate to civilian manufacturing jobs.
- Targeted Sector Investments: Allocates billions to shipbuilding, munitions, and drones to rebuild stockpiles and capacity.
Because the OBBBA and the National Defense Authorization bills passed, I am able to give Congress a grade of “B” instead of the “C” they earned because so many of the important bills mentioned above are stalled in their respective Committees. It is imperative that these bills be voted out of their respective Committees and brought forward into the House and Senate for a vote. My suggestion is to pick one of the above bills that you support and then call your Congressional Representative and Senator to urge them to support that bill. Remember, “We the People” are the basis for our Constitutional form of government. If “We the People” are silent and do nothing, then the lobbyists for the multinational globalist corporations and organizations will have the power to influence our elected representatives to support their interests to the detriment of the American people as a whole.