The week of March 12th, I was one of over 60 members of the Coalition for a Prosperous America (CPA) who attended our annual conference/fly-in. In a two-day blitz, members visited more than 120 House and Senate offices in Washington, D. C. to sound the alarm: “America’s massive, growing trade deficit is killing jobs, harming communities, and stifling economic growth.”
Our conference began Monday afternoon with remarks by CPA Chairman Dan DiMicco touting Present Trump’s announcement of imposing Section 232 tariffs on steel and aluminum as a long-overdue measure to safeguard our domestic steel and aluminum mills. He emphasized that CPA also supports all allowable trade enforcement remedies, such as the Section 201 Tariffs on imported solar panels and clothes washers and the Section 301 Investigation into Chinese intellectual property theft.
CEO Michel Stumo highlighted the new flyers covering issues that we were to discuss with Congressional Representatives and their staff. Research Director Jeff Ferry introduced the new Job Quality Index he has created, which will differentiate high-paying jobs from low-paying jobs in the monthly job data.
We urged Representatives to support legislation that would eliminate the nation’s trade deficit, address an overvalued dollar, provide stronger trade enforcement, and tackle troubling trade issues with China.
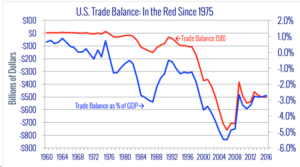
In our meetings, we provided Representatives and their staffs with legislative solutions aimed at eliminating America’s trade deficit, which grew to $566 billion last year. A fact sheet produced by CPA highlighted that no other country has run 42 years of consecutive trade deficits, which has been an average 2.99% drag on our Gross Domestic Product. The flyer offered key reasons why “free” and “fair” trade can result in balanced trade—instead of the job loss that has plagued America’s productive sectors for the past 15 years.
Another fact sheet, showed that ten countries account for 97% of our trade deficit, namely China, Mexico, Japan, Germany, Ireland, Vietnam, Italy, India, South Korea, and Malaysia. Our deficit with China alone jumped from a $337 billion deficit or 38% in 2016 to a $375 billion deficit or 47% in 2017.
We discussed how the he Tax Cuts for Jobs Act narrowed, but did not eliminate, the tax benefit for moving operations overseas, and presented information on how the tax system could be improved with Sales Factor Apportionment, based, which is “a destination of sales system used by many states that would tax corporate income in proportion to a companies’ sales in the U.S. regardless of either domicile or location of operations.” For example, a multinational corporation that still does 40% of its business in the U.S. would be taxed on the profits of that 40% of its worldwide sales.
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) was also another topic of discussion during our visits. CPA supports “mending it or ending it” as CPA has long argued that NAFTA has hurt U.S. manufacturing, cost jobs, and incentivized investment in Mexico rather than the U.S. We explained the provisions that must be included in a renegotiated NAFTA to help America’s manufacturers, such as reinstating country of original labeling for beef and pork, tightening country of origin rules to require higher North American content, requiring periodic reviews, and a mechanism for countries to withdraw, if necessary.
During our Hill meetings, we emphasized the importance to our national security of a vibrant domestic steel and aluminum industry. I mentioned that we outproduced Germany and Japan in World War II, but we would not be able to do so in future wars if we let our domestic steel and aluminum industries be further decimated. We expressed our support for President Trump’s tariffs on steel and aluminum import, especially since CPA has many members in the steel industry.
In addition, we discussed the problem of the overvalued U. S. dollar. And presented the flyer that showed as of May 2017, the U. S. dollar was overvalued by 25.5%, whereas the currencies of Japan and Germany were undervalued by nearly as much, with South Korea not far behind at about 15% of undervaluation. I told them that CPA has a new Advisory Board member, Dr. John R. Hansen, who is a 30-year veteran of the World Bank. He has proposed a solution to address this problem that “pushes American wages down, increases the trade deficit, disrupts capital markets, and hooks consumers on debt.” He proposed that “Congress should provide the Federal Reserve the responsibility to maintain the dollar at a current account balancing equilibrium price. New legislation should provide the Fed with a new tool to moderate the dollar exchange rate called a market access charge (MAC).” He projects that the MAC would balance trade in five years and that balance would be maintained in the future.
In addition to our congressional visits, CPA hosted a bipartisan group of Representatives to meet with our members, including Rep. Tom Reed (R-NY-23), Rep. Dan Lipinski (D-IL-23), Rep. Mo Brooks (R-AL-05), and Rep. Robert Pittinger (R-NC-09). Last fall, Representatives Brooks and Lipinski introduced House Congressional Resolution 37 for Congress to set a national goal to eliminate the trade deficit. It is only one sentence long: “Expressing the sense of Congress that Congress and the President should prioritize the reduction and elimination, over a reasonable period of time, of the overall trade deficit of the United States.”
Rep. Pittinger is co-sponsor of HR 4311, the Foreign Investment Risk Review Modernization Act of 2017, which would expand and update the review by the Committee on Foreign Investment in the U.S. (CFIUS) to meet new national security risks. As we distributed this flyer to Congressional Members, we expressed our support for the order President Trump signed to prohibit the acquisition of Qualcomm by Broadcom. When I met with Congressman Duncan Hunter, he said he had sent a letter to President Trump urging him to stop the takeover of Qualcomm by Broadcom.
As the publisher of my newest book, Rebuild Manufacturing – the Key to American Prosperity, CPA provided books for me to present at my 15 appointments with Congressional Members and/or staff, and I also had the pleasure of presenting a copy of my book to Rep. Mo Brooks and Rep. Robert Pittinger.
On March 16, CPA released a press release about the success of the annual conference fly-in. highlighting the following:
“The 2018 CPA fly-in was our best yet,” said Dan DiMicco, CPA Chairman. “The presentations and panels were very well received and by far the most informative yet, with great speakers and panelists. Without a doubt we made a strong impact on those we visited on the Hill. Our congressional speakers clearly showed us that our messaging is having an impact.”
Michael Stumo, CEO of the CPA said, “We came to Capitol Hill with a united message from our members that Main Street America urgently needs action on trade. We were encouraged to find that our elected officials are becoming more receptive to calls for greater trade enforcement. Our next step is to remind them that voters are watching, and that the time for action is now.”
CPA chair Dan DiMicco said, “In 2016, voters spoke very clearly at the ballot box. They are frustrated and tired with the business-as-usual approach in Washington. We came to Capitol Hill this week to remind our elected officials that the American people are waiting for action, and that reducing our mammoth trade deficit must be a top priority.”
“The Coalition for a Prosperous America trade conference was very useful and successful in educating our members and legislators about the dangers of continuing our country’s obsession with free trade,” said Roger Simmermaker, author of How to Buy American and a CPA member. “Several times, it was evident that many members of Congress and their staff experienced what I would call “light bulb moments” as we laid out our ideas and strategies for a better and fairer trade policy that will benefit our national economy.”
“When real workers, manufacturers, and agriculturalists converge on Washington, theory is tested against reality, and good things begin happening in America,” said Bill Bullard, CEO of R-CALF and a CPA board member. “There is no question that CPA had a positive impact on U.S. trade policy this week.”
The steel and aluminum tariff discussions proved particularly wide-ranging. And as Greg Owens, CEO of Sherill Manufacturing and a CPA member, noted, “Trade and our decades-long deficits are a critical and complex issue. While I applaud the recent move to levy tariffs on steel and aluminum, the comprehensive answer must go beyond that. The overvalued dollar and tax policies are major contributors to the problem that must be addressed. CPA has detailed concrete solutions to these and other issues that I fully support. It was a privilege and an honor to help CPA introduce and develop these solutions on Capitol Hill this week.”
I am proud to be one of the 4.1 million members in the manufacturing, labor, and agricultural sectors who are “united in their view that a continuing trade deficit hampers jobs and productivity nationwide. CPA will continue to urge action on America’s troubling trade deficit, and we look forward to expanding its relationship with Members of Congress who have pledged to fight for America’s manufacturers, farmers, and their workers.”
Chairman Dan DiMicco and CEO Michael Stumo will be in southern California April 18 – 20th speaking to members of Metal Service Center and NTMA, as well as speaking at the San Marcos Manufacturing Summit to be held at the San Marcos Community Center on Friday, April 20th. As Chair of CPA’s California chapter, I invite you to register to attend.
 Source: Coalition for a Prosperous America
Source: Coalition for a Prosperous America