“You were ahead of the curve on trade.” This was the common refrain heard last week by members of the Coalition for a Prosperous America who attended our annual fly-in to Washington, D. C. We had eight teams of members visiting Congressional Representatives and Senators on March 14th and 15th. As Chair of our developing California chapter, it was my fifth year attending the CPA fly-in, and our simple message of eliminating the trade deficit resonated well in the halls of Congress.
No one could deny that we have a huge deficit as shown on the chart below:
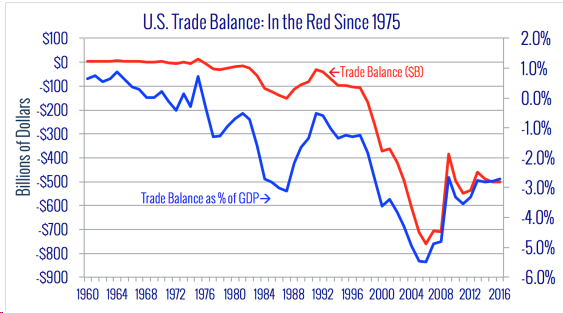
The annual trade deficit has reduced our U. S. GDP by some 3% to 5.5% each year, and those reductions compound over time.
There is no historical record of any other country in history running 41 years of consecutive trade deficits. Why is this important? Because every billion dollars of net imports costs 4,500 American jobs according to conservative estimates. So last year’s $502 billion deficit equates to 2.25 million jobs lost.
As a result, our Labor Force Participation is in serious decline. The U. S. is the only G7 nation with a DECLINE in LFPR since 1998 for workers ages 15-64. It peaked at 77.4% in 1998 and dropped down five points to 72.6% in 2015, meaning that over 7 million people dropped out of labor force since 1998.
The remedy recommended by the Coalition for a Prosperous America is simple: Congress should establish a national goal to eliminate the trade deficit.
Balanced trade over time is the goal of free trade and of fair trade. Balanced trade will re-industrialize our country, enable massive job creation, grow our wealth and effectively neutralize foreign mercantilism. Trade policy must address true drivers of deficit, these countries and their practices. Many of these countries have export-oriented growth strategies in which they rely upon the US market to consume their exports rather than increasing their internal consumption. China, Germany, Japan and other countries pursue net exports through strategic mercantilism, not free trade. Currency manipulation, value added taxes, state influenced enterprises, and other
tactics are used.
The following top 10 countries account for 90% of America’s 2016 goods trade deficit:
| Rank | Country | 1992 Deficit | 2016 Deficit | Change 1992-2016 |
| 1 | China | -$18B | -$355B | -$337B |
| 2 | Mexico | -$6B | -$115B | -$121B |
| 3 | Japan | -$50B | -$75B | -$25B |
| 4 | Germany | -$8B | -$70B | -$62B |
| 5 | Canada | -$15B | -$58B | -$53B |
| 6 | Ireland | +5B | -$36B | -$37B |
| 7 | Vietnam | $0B | -$34B | -$34B |
| 8 | South Korea | -$2B | -$30B | -$30B |
| 9 | Italy | -$4B | -$30B | -$26B |
| 10 | India | -$2B | -$30B | -$28B |
Note: These figures are based on U.S. Commerce Dept. data subtracting Imports for Consumption from Domestic Exports which are intended to strip out goods that enter and leave the U.S. simply for re-export, without having any significant value added to them inside the U.S.
Currency manipulation and misalignment are key tactics that the above countries use to gain an advantage in trade. Currency manipulation is trade cheating, because it is both an illegal tariff and a subsidy.
Foreign governments intervene in foreign exchange markets by buying dollars. More than 20 countries have intervened in foreign exchange markets to undervalue their currencies in the past ten years. These countries account for one-third of the world economy and two-thirds of the world’s current account surpluses. Gagnon has calculated that “A country’s current account balance increases between 60 and 100 cents for each dollar spent on intervention.”
“The largest loser is the United States, whose trade and current account deficits have been $200 billion to $500 billion per year larger as a result. The United States has thus suffered 1 million to 5 million job losses.” (Bergsten, 2012) The U. S. economy cannot produce jobs and wealth without addressing this problem. The Coalition for a Prosperous America proposes the following solutions:
• U.S. trade enforcement law should treat currency undervaluation as a countervailable subsidy
• Tariffs should be applied against currency manipulators to neutralize their unearned advantage
• Government policy should pursue a dollar priced at equilibrium rather than accept a persistently overvalued dollar
• Trade agreements should include effective controls on currency manipulation and misalignment
Border Adjustable Consumption Taxes (aka VATs) are a tariff by another name. They are allowed under WTO rules and range from 12% to 24% with the average being 17% globally. This means that virtually all foreign countries tax our exports at this average 17% VAT. They subsidize domestic shipments abroad with rebating the VAT to their manufacturers. The U.S. does not have a VAT to offset this advantage.
Consumption taxes are a tax on consumption as opposed to income, wealth, property, or wages. A Goods and Service Tax (GST) and a Value Added Tax (VAT) are consumption taxes. They are usually a tax only on the “value added” to a product, material, or service. Over 150 countries have such taxes, but the U. S. does not.
The U. S. negotiated tariff reductions or elimination in good faith with our trading partners under NAFTA and the Central America Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA, but Mexico instituted a 15% VAT, and Central America established a 12% VAT.
After 40 years of tariff reduction under various trade agreements, other countries replaced tariffs with VATs, but the U. S. did not. Thus, American exporters face nearly the same border taxes as they did in the early 1970s.
To solve this problem, the Coalition for a Prosperous America proposes that Congress implement a border adjustable consumption tax (VAT) and use the proceeds to credit against the payroll taxes paid by all workers and businesses. The benefits would be:
• Reduce the cost of labor in the U.S.
• Give every worker a raise
• Lower the price of U.S. exports
• Levy a tax on imports
In President Obama’s 2016 budget, Payroll Taxes were projected to be 31% of the revenue or $1.11 trillion. If a 12.9% VAT were set, it would produce approximately $1.45 trillion in tax revenue, completely offsetting the revenue from Payroll Taxes. All Payroll Taxes could be eliminated with a credit. With a 15% VAT, other tax reform or domestic production cost reduction could be funded. European Union countries use their VATs to provide another revenue stream to allow them to reduce their corporate taxes to be more globally competitive.
The benefit of giving a Payroll Tax credit out of VAT funds is that it would offset the regressiveness of a VAT by elimination of the regressive Payroll Tax. There would be no impact on prices of domestic goods and services, but prices of imported goods and services would increase. This would incentivize consumers to buy Made in USA products instead of imports. In addition, it would reduce the cost of production for U. S. producers enabling them to be more competitive in the global marketplace.
Our Coalition members also encouraged Congress to reinstate the Country of Origin Labeling (COOL) that was struck down by an unelected foreign tribunal of the World Trade Organization. Congress caved in to the WTO ruling and passed repeal legislation that exceeded the WTO ruling eliminating COOL for beef and pork, as well as for ground beef and ground pork.
Canada and Mexico want to export their cattle, hogs, beef, and pork to the U. S. without informational labeling that reveals where the cattle and hogs were born, raised, and slaughtered. Right now, meat packers are able to import cattle and hogs and slaughter them to get the USDA stamp. Consumers want to know where cattle and hogs were born and raised, not just slaughtered for reasons of food safety.
Congressional Representatives and Senators need to have the courage to reinstate COOL and vigorously defend our national sovereignty and consumer choice against international interference. COOL legislation enables consumers to Buy American in the grocery store. It prevents consumer deception and empowers consumers to buy food produced under the safety regime of their choosing. It would help to jumpstart America’s ailing rural economy through supporting domestic producers and preventing industry consolidation.
The final message that is critical is that the U. S. must modernize its foreign investment rules to protect American companies that are critical to our national security and economic security. Investors from countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are making strategic acquisitions of U. S. companies and land that threaten our security and future prosperity. These same countries either severely restrict or do not allow 100% acquisition of companies in their country. The Committee on Foreign Investment in the U.S. (CFIUS) can block incoming investment based upon national security concerns, but not for economic strategy reasons as other countries do.
Congress must update the laws governing foreign investment to include economic security and allow longer review periods, beyond 30 days, for CFIUS to review proposed investments. This would allow more time to gauge systemic threats to U. S. interests in addition to individual cases. The legislation should include a “net benefit” test to encompass American economic interests where proposed acquisitions of companies that are important to future U. S. technology and employment are concerned (both civilian and defense related).
The question now is – Will Congress have the courage to take the bold action needed to eliminate the trade deficit, address currency manipulation, reinstate COOL and control foreign investments? Time will tell.