You may feel that there is not much you can do as an individual to rebuild American manufacturing to create jobs and protect our national security. This isn’t true? Remember that our country was founded by a small group of people that did indeed change the world by forming the United States of America. American activist and author, Sonia Johnson said, “We must remember that one determined person can make a significant difference, and that a small group of determined people can change the course of history.” Eleanor Roosevelt echoed this sentiment saying, “Never doubt that a small group of thoughtful, committed citizens can change world; indeed, it’s the only thing that ever has.”
Here are suggestions of what each one of us can do:
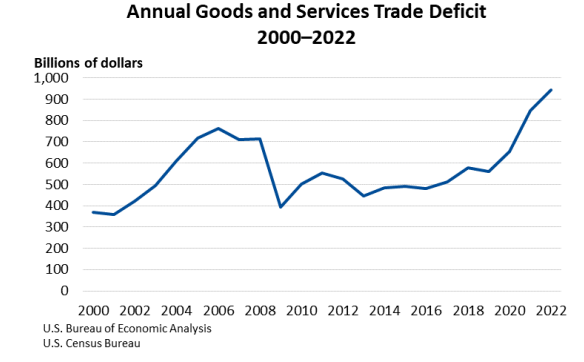
As a Consumer: It matters if we buy American-made products. Our addiction to imports has played a major role in creating our high trade deficit, especially with China, where most of the consumer goods we import are manufactured.
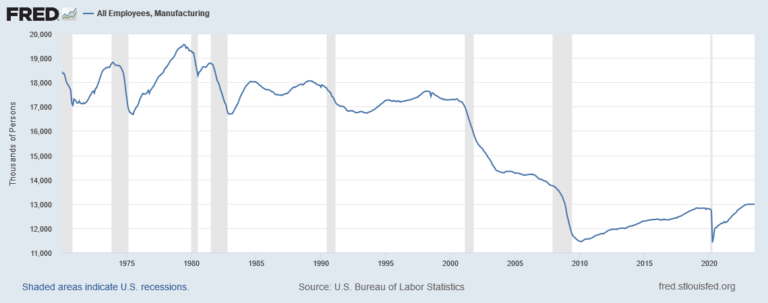
We lost 5.8 million manufacturing jobs from 2000 – 2010 because of importing so many goods from China and other Asian countries. In contrast, American-made products create American jobs, reduce our trade deficit, and reduce our budget deficit from increased tax revenue. Each time you choose to buy an American-made product, you help save or create an American job.
When you shop in person, look for the country-of-origin labels of goods. Most imported goods are required to have these labels. Don’t throw things into your shopping cart without checking labels. The most important step is to make a commitment to buy American made products. Commit to make a fair effort to find made in the USA products. Make a promise to yourself to buy the “Made in USA” product even if it costs more than the imported product. It is a small sacrifice to ensure the well-being of your fellow Americans. The price difference you pay for “Made in USA” products keeps other Americans working.
If the product you are looking for is no longer made in America, then buy the product from another country besides China, which has nuclear warheads aimed at American cities. By buying Chinese imports, American consumers have provided the funds for the bulk of China’s military buildup. American service men and women could one day face weapons mostly paid for by American consumers. Instead, you could patronize impoverished countries such as Bangladesh or Nicaragua, which have no military ambitions against the United States.
In addition, by buying a product “Made in USA, you would reduce the “carbon footprint” caused by shipping the product thousands of miles by container ship, using a greater amount of fossil fuel than shipping within the United States.
If you are willing to step out of your comfort zone, you could ask to speak to the department or store manager of your favorite store and tell them that they need to start carrying more “Made in USA” products if they want to keep you as a customer. If you buy products on line or from catalogs, you could contact these companies via email with a similar message. Your communicating with a company does have an effect because the rule of thumb in sales and marketing is that one reported customer complaint equals 100 unreported complaints.
If you think that Americans no longer care about where goods are made or have concerns about the safety of foreign products, you may be surprised to learn that poll after poll shows that the majority of Americans prefer to buy American.
A survey of 1,000 U.S. adults by Morning Consul in May 2023 with regard to their views of products made by American companies vs. Chinese companies revealed the following:
- 65% of U.S. adult consumers claimed to sometimes or always buy “Made in America” products intentionally
- 43% prioritize purchasing American-made products rather than prioritizing other options like quality, sustainability, or affordability
- 48% are willing to pay higher amounts for U.S.-based products. 39% responded they would pay between 6%-10% more for said products
If you are having trouble finding “Made in USA” products, you can search “buy American” on the internet. A few of the sites you will find are:
www.ionlybuyamerican.com
https://www.themadeinamericamovement.com/made-in-usa-companies/
https://www.madeinamerica.co/pages/thelist
https://madeinamericastore.com/home/
There are also brick and mortar stores springing up around the country that are either stocking only “made in America” products, such as the Buy American Store and the Urban Outfitters stores. Even stores like Wal-Mart and Target are carrying more “Made in USA brands due to customer demand.
As American consumers, you have many choices to live safely and enjoy more peace of mind with American products. It’s high time to stop sending our American dollars to China while they send us all of their tainted, hazardous, and disposable products. If 200 million Americans refuse to buy just $20 each of Chinese goods, that’s a four-billion-dollar trade imbalance resolved in our favor – fast!
As a Voter: Voter apathy is partially responsible for the state of our affairs as a country. Too many people have decided that there is nothing they can do on an individual basis and have stopped voting.
Americans have been “sold down the river” by politicians on both sides of the aisle – Democrats and Republicans. Democrats profess to support “blue collar workers” and unions, yet NAFTA and the WTO treaties were approved and went into effect under the presidency of Democrat Bill Clinton. Republicans have professed to support business, yet they have voted to approve harmful trade agreements like NAFTA and have primarily supported policies that benefit large, multinational corporations rather than the small businesses that are the engine of economic growth in the U.S. and the foundation of the middle class.
Remember that the U.S. President isn’t a king or dictator; there are only a limited number of actions a president can do by Executive Order. It’s the job of the President’s administration to set policies, but Congress turns the policies into laws. This makes it just as important to choose to vote for the right person for your Congressional Representative and Senator as it to vote for the President because very few of the policies proposed by the President will be turned into law if Congress is controlled by the opposition party.
In order to help manufacturers succeed and grow to rebuild our domestic manufacturing industry, manufacturers need affordable corporate tax and interest rates because manufacturing is a capital-intensive industry. They need affordable and reliable energy sources because it takes energy to manufacture every product. They need protection from the unfair trade practices of China, such as:
- Currency Manipulation – undervaluing the yuan against the U.S. dollar to capture market share with lower prices
- Product Dumping – selling at or below cost to destroy their American competitors.
- Trans-shipping – shipping to an intermediary country before shipping to the U.S. from that country in order to hide that the product was made in China.
When you choose who to vote for President or Congress, examine both their campaign promises and their track record. It’s important to support candidates that would support and protect American manufacturers. Here are a few questions you can ask:
- Do they support more harmful trade agreements?
- Will they increase enforcement of current Agreements to reduce trade cheating?
- Will they enforce penalties on trans-shipping of steel and aluminum?
- Will they continue the tariffs on Chinese steel, aluminum, solar panels and add tariffs on other goods imported from China?
- Will they support “Buy America” for all government agencies and not just the military?
- Will they keep tax rates at an affordable level?
- Will they institute policies to provide affordable and reliable energy produced in the U.S.?
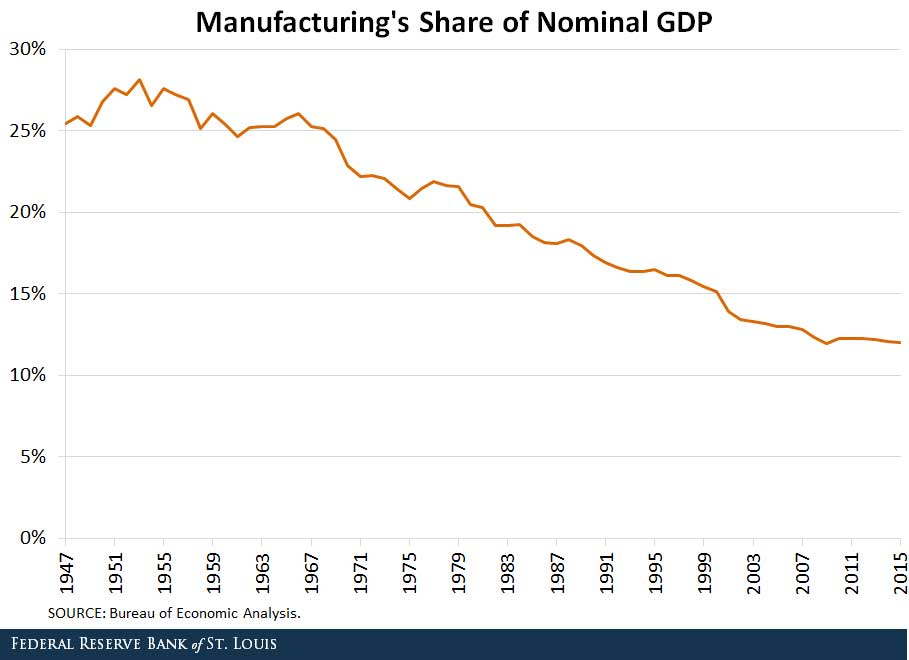
We cannot afford to export our wealth and be able to remain a first-world country. We cannot lose our manufacturing base and be able to remain a “superpower.” In fact, we may not be able to maintain our freedom as a country because it takes considerable wealth to protect our freedom.
You can play a role as an individual in saving our country ? the company you save or the job you save by your actions may be your own in the future. It’s time to shed apathy, become involved, and vote for the candidate that will best protect American manufacturers and help rebuild American manufacturing.